On December 22, 2016, NASA decided to suspend the March 2016 launch of the InSight Mars lander because a key instrument lost its pressure seal during testing.
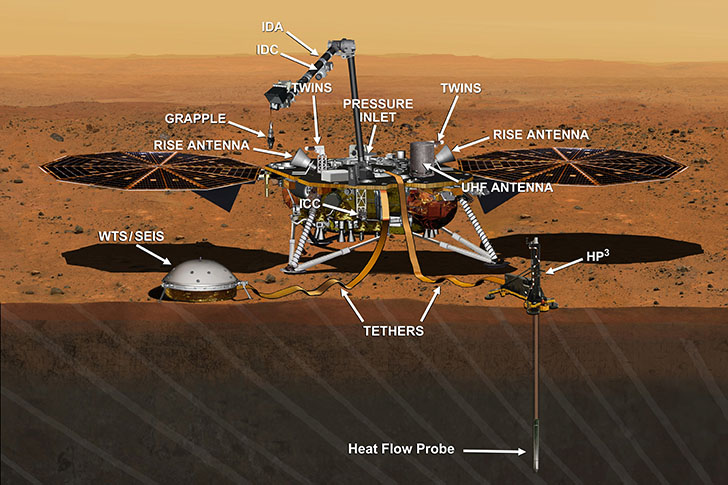
The instrument involved is the Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS), a seismometer provided by France’s Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES). Designed to measure ground movements as small as the diameter of an atom, the instrument requires a vacuum seal around its three main sensors to withstand the harsh conditions of the Martian environment.
A leak earlier this year that previously had prevented the seismometer from retaining vacuum conditions was repaired, and the mission team was hopeful the most recent fix also would be successful. However, during testing on Monday in extreme cold temperature (-49 degrees Fahrenheit/-45 degrees Celsius) the instrument again failed to hold a vacuum.
InSight’s science payload includes two key instruments: SEIS, provided by CNES, and the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3), provided by the German Aerospace Center (DLR).
SEIS was built with the participation of the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris (IPGP) and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH), with support from the Swiss Space Office and the European Space Agency PRODEX program; the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS), supported by DLR; Imperial College, supported by the United Kingdom Space Agency; and JPL.