1. Real-Time Posture Detection
AI enables immediate posture monitoring by leveraging computer vision and sensors to identify misalignments as they happen. Modern apps can map a user’s skeletal alignment in real time through smartphone cameras or wearables, alerting users the moment they start to slouch or assume a risky position. Instant feedback means users can correct their form on the spot, preventing strain before it accumulates. This continuous detection-and-correction loop helps build muscle memory for proper posture. As AI models and device sensors improve, real-time posture detection is becoming more precise and accessible in everyday settings.
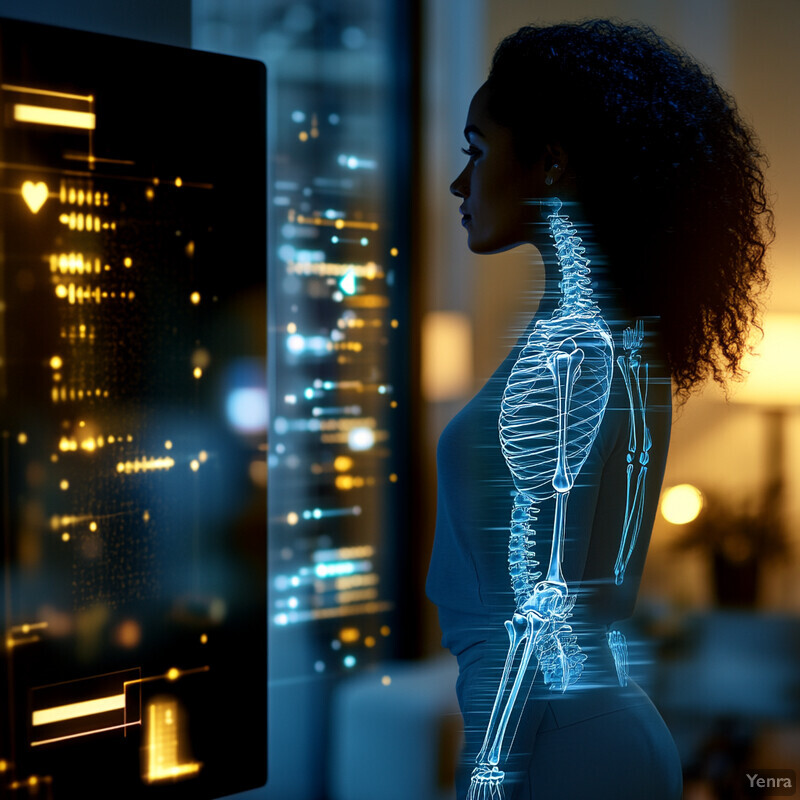

AI-driven systems can now detect postural deviations with extremely high accuracy and speed. In one 2023 study, a smart cushion with embedded pressure sensors combined with machine learning identified improper sitting postures with 99.99% accuracy. Likewise, a 2025 vision-based approach using a standard camera achieved real-time performance (~55 milliseconds per frame) and maintained 97.5% accuracy in counting exercise repetitions, even improving pose detection accuracy by 15% under poor lighting conditions through adaptive image enhancement. These advances highlight how real-time AI monitoring can reliably catch slouching or misalignment and prompt immediate correction.
2. Personalized Exercise Recommendations
AI tailors corrective exercise routines to an individual’s unique needs, replacing one-size-fits-all plans with data-driven personalization. By analyzing a user’s posture issues, fitness level, and mobility constraints, smart coaching apps suggest exercises that target the user’s specific muscle imbalances or flexibility limitations. This means someone with rounded shoulders might get shoulder and upper-back strengthening moves, while another person with tight hip flexors receives hip-opening stretches. The recommendations evolve as the user progresses – becoming more challenging or introducing new exercises as posture improves. Personalized plans keep users engaged and address root causes of their poor posture, leading to more effective and sustainable improvements.
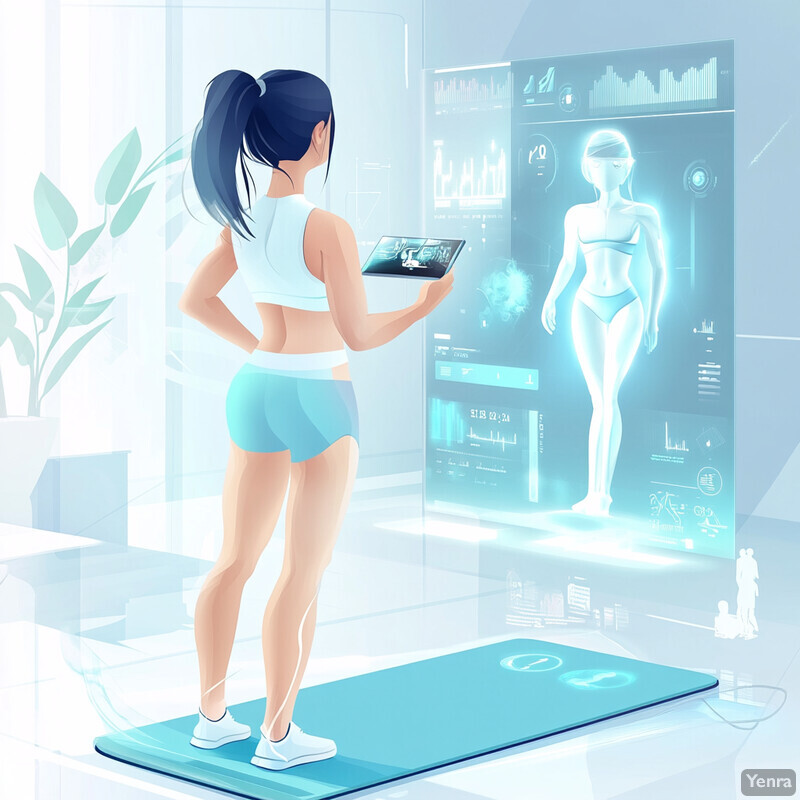

Customized AI guidance has been shown to improve exercise outcomes significantly more than generic routines. In a 2023 randomized trial, participants using an AI-driven coaching app that provided feedback on squat form saw their posture scores jump from near 0 to 8 (on a 10-point scale) after 2 weeks, whereas a control group following standard exercise videos showed no significant improvement i-jmr.org . The AI tailored exercises to each user’s weaknesses and adjusted with their progress, resulting in better form and joint alignment (for example, users in the AI group markedly improved their knee angles during squats while the control group did not i-jmr.org ). On the industry side, major fitness platforms are embracing hyper-personalization through AI. For instance, in 2025 the company Echelon launched a generative AI–powered coach that allows users to simply talk to a chatbot to modify their workout plan, such as swapping out a 45-minute session for a shorter one, using natural voice commands. This trend toward real-time, voice-enabled personalization underscores how AI is delivering “made-for-you” exercise recommendations at scale.
3. Intelligent Feedback Loops
AI creates a continuous feedback loop during training – detecting posture errors and immediately cueing the user to adjust, then learning from the user’s response. These intelligent feedback systems act like a virtual coach in the room, providing gentle nudges (“straighten your back” or “relax your shoulders”) right when needed. Immediate, data-driven feedback helps users correct mistakes in real time rather than after the fact. Over time, the AI can refine its feedback based on the user’s improvements or struggles, effectively “learning” the user’s behavior. This closed-loop coaching accelerates habit formation: users are consistently reminded until proper posture becomes second nature. In short, intelligent feedback turns passive exercise into an interactive, guided experience that keeps users mindful of their alignment at every moment.
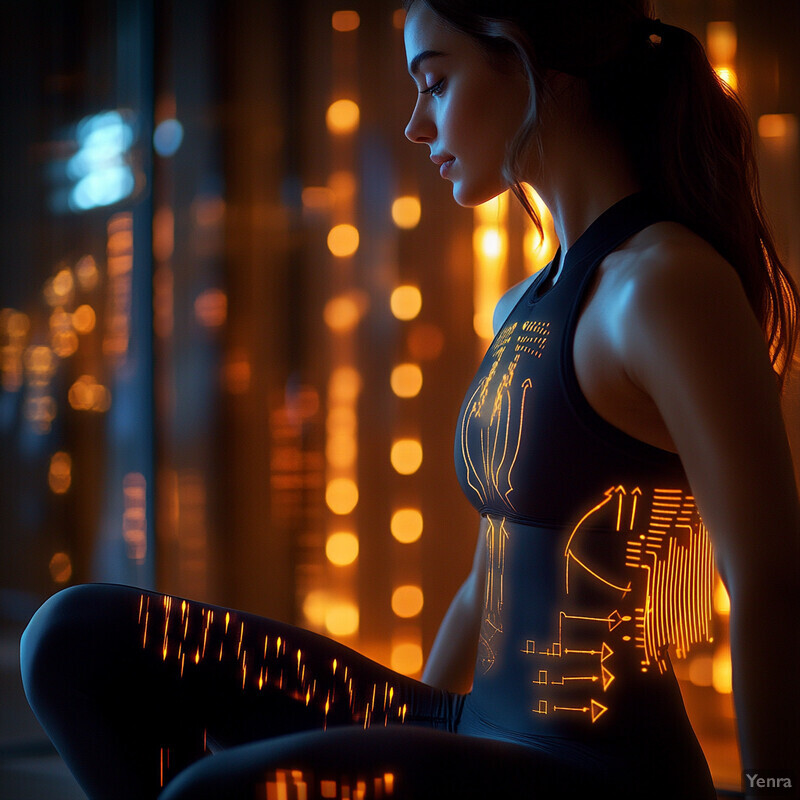

Real-time corrective feedback has measurable benefits on posture training outcomes. In a 2024 experiment on forward head posture, users who received instant feedback from an AI sensor system showed a significant improvement in neck alignment – their craniovertebral angle increased by 3–5 degrees, indicating a more upright head position, an improvement comparable to outcomes from supervised physical therapy exercises. This kind of immediate cue (“chin tuck” reminders whenever their head drifted too far forward) helped participants attain results on par with doing dedicated exercise routines. Beyond sensors, wearable devices and smart apparel now offer continuous feedback through multiple channels. Research in 2024 noted that wearables can deliver real-time corrective feedback via auditory signals, on-screen prompts, or haptic vibrations whenever a user adopts an incorrect posture. These instant alerts, whether a gentle buzz or spoken cue, prompt users to self-correct in the moment. By ensuring users don’t unknowingly remain in a harmful position, intelligent AI feedback loops greatly accelerate the adoption of healthier postural habits.
4. Adaptive Difficulty Levels
AI ensures that posture exercises stay safe and appropriately challenging by dynamically adjusting difficulty based on the user’s performance. If a beginner is struggling with an exercise, the app might reduce the intensity or suggest an easier variation; as the user gets stronger and more stable, the AI will increase the difficulty (for example, introducing more reps, resistance, or balance challenge). This adaptive progression prevents frustration and injury that can occur from exercises that are too hard, while also avoiding plateaus that result from routines that become too easy. Essentially, the app “spots” the user much like a personal trainer would – easing off when form breaks down and ramping up when the user is ready. The result is a personalized difficulty curve that keeps the user in the optimal zone for improvement, promoting steady gains in strength and posture without overexertion.

Adaptive difficulty has been shown to improve both user compliance and outcomes in exercise programs. In a 2024 feasibility study of a graded-challenge rehab program, an AI-driven system continuously increased or decreased exercise difficulty based on the patient’s real-time performance. The results were impressive: the system had 92% uptime and delivered 99% of prompts successfully, with patients responding to the prompts almost immediately 98% of the time. Participants remained highly engaged (performing prescribed movements on 98% of cue alerts) and reported strong confidence in their abilities by the program’s end, reflecting the system’s success in keeping challenges appropriately tailored. In consumer fitness, we see similar adaptive approaches. For example, the AI coach of one training app analyzes recovery data (like heart rate variability and user fatigue) each morning and will proactively adjust that day’s workout – if the user is run-down, the AI might replace a high-intensity interval session with a lighter aerobic run to maintain progress without overtraining. By listening to the body’s signals and scaling difficulty up or down, AI ensures users are continually progressing toward better posture in a safe, sustainable manner.
5. Predictive Injury Prevention
AI isn’t just correcting current posture – it’s looking ahead to predict and prevent injuries before they happen. By analyzing patterns (like consistently uneven weight distribution, repetitive motions, or frequent forward-head posture), advanced apps can identify risk factors that might lead to pain or injury over time. The system can then alert the user (“Your lower back is under strain when you lift objects”) and recommend preventative measures, such as targeted stretches, strengthening exercises, or adjustments in technique. This predictive approach transforms posture correction from reactive (fixing issues after pain arises) to proactive (addressing issues in advance). In workplaces and sports, such AI tools help create safer movement habits and can reduce the incidence of common injuries like back strain, neck pain, or repetitive stress injuries by nipping risky behaviors in the bud.
The need for preventive posture correction is substantial – in the United States alone, there were over 500,000 musculoskeletal disorder cases in a single year that were serious enough to require days off work. Poor posture and body mechanics are major contributors to these injuries. AI-driven posture monitoring systems are now being deployed in manual labor and office settings to mitigate such risks. A 2024 system, for example, integrates AI with real-time video analysis of workers lifting and moving. Its goal is to improve workers’ form and reduce musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) risk by providing immediate feedback and risk alerts. Early implementations have shown concrete benefits: companies report fewer injury incidents after rolling out AI posture coaching. In one pilot, an AI ergonomics platform that detected and warned about unsafe lifting techniques saw a 25% drop in lifting-related injuries over just six months. By anticipating strain points (like a habit of twisting while lifting or a tendency to crane the neck forward at a computer), AI can recommend timely adjustments and exercises, effectively cutting off injuries before they occur.
6. Dynamic Motion Analysis
AI enables detailed breakdowns of complex movements to help users refine their overall motion and posture through an exercise. Rather than just static snapshots, dynamic motion analysis looks at how you move through space – evaluating joint angles, velocities, and coordination in real time. For instance, during a lunge or a yoga flow, the app can analyze each phase of the motion (descent, hold, ascent) for balance and symmetry. Users receive insights like “your weight shifted to the left” or “your knee angle is too acute at the lowest point,” which were previously only discernible with professional gait labs or high-end sports analyses. This level of analysis helps users not only hold a correct static posture but also maintain proper alignment throughout movement transitions. In essence, AI-powered motion analysis brings professional biomechanical assessment into the home, guiding users to move with better form and fluidity and thereby preventing dynamic posture problems (like twisting or jerking) that could lead to injury.
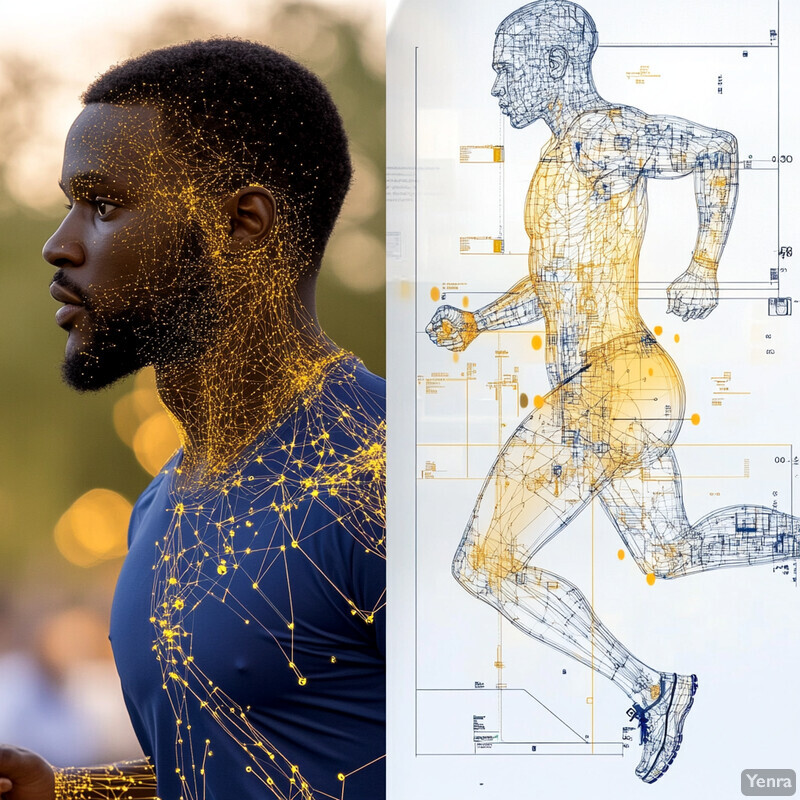

Recent AI advancements have achieved lab-level accuracy in analyzing human motion using everyday devices. In 2024, researchers validated a markerless smartphone video system for measuring joint kinematics during exercises and found it to be extremely precise. The AI system’s estimates of hip and knee joint angles during a jump were almost identical to those from a gold-standard motion capture lab – showing Pearson correlation coefficients of 0.96 for hip angle and 0.99 for knee angle compared to the laboratory reference kops.uni-konstanz.de . The error margins were only a few degrees. This demonstrates that a simple phone camera with AI can capture detailed movement quality (like the angle of your hips, knees, and ankles throughout a jump or squat) with high fidelity kops.uni-konstanz.de . Armed with this kind of detailed data, posture apps can score the quality of each rep, detect subtle asymmetries or instability, and give granular feedback (e.g., “your left knee caved in 5° on that squat”). Dynamic analysis powered by AI thus makes it possible for users to receive expert-level critiques on complex movements, helping them improve not just static posture but the quality of their movement patterns.
7. Multi-Device Integration
AI-driven posture apps increasingly operate across an ecosystem of devices to provide a 360° view of a user’s posture habits. Rather than relying on a single sensor, they pull data from multiple devices – for example, a smartwatch tracking your physical activity and heart rate, a smart chair or standing desk sensor monitoring your sitting posture, and your phone’s camera analyzing your exercise form. By unifying these data streams (often via the Internet of Things), the AI can contextualize posture: it knows how long you’ve been sedentary at work, how well you slept (from a sleep tracker), and even your stress levels, and it uses this information to tailor recommendations. Multi-device integration means your posture app doesn’t exist in isolation – it “talks” to your calendar to find free moments for stretch breaks or uses your car seat sensor to remind you to adjust posture during long drives. This holistic approach yields more personalized and effective posture coaching because it considers the full picture of when, where, and how your posture could be improved throughout the day.

The proliferation of connected devices has made this integrated approach feasible. By the end of 2024 there will be nearly 18.8 billion IoT-connected devices in use globally iot-analytics.com – a massive network that posture correction systems can tap into for data. We’re already seeing practical applications of multi-device integration in healthcare. For instance, in assistive technology for wheelchair users, sensors built into the wheelchair combined with AI allow simultaneous, objective assessment of a user’s sitting posture and their functional status (like pressure distribution and movements). This integrated data is then shared with both the user and health professionals, enabling early interventions – the AI might notice, for example, that a patient tends to lean heavily on one side and alert a therapist to adjust the wheelchair cushion or prescribe exercises to avoid pressure ulcers. Likewise, a posture app might integrate phone and wearable data: your smartphone detects slouching via camera while your smartwatch notes you’ve been inactive for 2 hours, triggering the app to suggest a posture break. Such multi-device ecosystems create a richer, context-aware posture profile and ensure recommendations fit seamlessly into the user’s daily life across all their devices.
8. Behavioral Insights and Coaching
AI-powered posture apps don’t just monitor your body – they also learn about your behavior and motivation, using that insight to coach you more effectively. By tracking when you use the app, when you skip exercises, and even your mood or feedback, the system identifies patterns (for example, “User tends to skip evening sessions” or “posture improves on days with reminders”). Using principles from behavioral psychology, the app can adapt its coaching style – maybe offering encouragement or adjusting goals – to keep you engaged. Some apps incorporate readiness questionnaires or use AI to infer your stage of change (whether you’re just thinking about fixing your posture or actively doing it). With these insights, the coaching becomes hyper-personalized: an AI might send a motivational message if it predicts you’re losing interest, or congratulate you at strategic times to reinforce consistency. Essentially, the app acts as a behavioral coach, not just a posture tracker, employing strategies like positive reinforcement, habit formation techniques, and even gamified challenges tailored to what best motivates you. This intelligent coaching approach increases adherence and helps make good posture a lasting habit rather than a short-term experiment.

Emerging research shows that AI coaches grounded in behavioral science can significantly boost user engagement and success. A striking example comes from Stanford University in 2025: researchers developed an AI wellness coach that fine-tunes motivational messages to a user’s psychological “stage of change.” In a controlled study with over 600 participants, 85.4% preferred the AI-generated motivational messages over human-written ones when given generally, and 68% of users favored the AI’s advice when it was personalized to their readiness stage. Importantly, expert evaluators rated the AI’s messages as far more effective and aligned with behavior-change principles compared to standard messages (the AI messages scored 4.4 out of 5 for effectiveness vs. 2.8/5 for human messages). These results demonstrate the power of AI-driven behavioral insight: the system “understood” users’ mindsets and delivered coaching that not only resonated better but was objectively more effective in driving healthy behavior. In practical terms, this means a posture app’s AI coach might detect if a user is demotivated (perhaps usage data show a drop-off) and respond with a tailored nudge like, “Feeling the slump? Remember, a 2-minute stretch can boost your energy!” – a message crafted from both the user’s data and proven psychological models. By incorporating behavioral insights, AI coaches are keeping users motivated and on track in ways that generic reminders never could.
9. Virtual Physical Therapy Sessions
AI is enhancing telehealth and virtual physical therapy (PT), making remote posture correction and rehabilitation highly effective. Instead of needing in-person visits, users can perform therapist-prescribed exercises at home while the app’s AI watches their form via camera and provides guidance – essentially bringing the physical therapist’s eyes into your living room. These virtual sessions can be live (with a remote therapist supervising multiple patients through AI) or asynchronous (the AI monitors and later reports to your clinician). AI ensures patients do exercises correctly and can even measure range of motion or improvements over time, data which is shared with healthcare providers. This approach dramatically improves access – people in rural areas or with busy schedules can get high-quality PT from home – and studies are showing outcomes comparable to in-person therapy. Additionally, AI can triage and personalize the rehab program continuously, for example, by increasing exercise difficulty as a patient’s condition improves or flagging to a human therapist if progress stalls. In short, AI-powered virtual PT extends expert posture and rehab guidance beyond clinic walls, maintaining quality of care while adding convenience and continuous monitoring.

Virtual and AI-assisted physical therapy is proving its worth in clinical results. A 2022 systematic review encompassing over 200,000 patients found that tele-rehabilitation programs produced consistently positive outcomes across a variety of conditions, essentially matching the effectiveness of traditional in-person rehab in many cases. Patients receiving remote therapy achieved improvements in pain, function, and mobility that were on par with clinic-based care, but with the added benefits of accessibility and convenience. Moreover, integrating AI into home-based rehab can amplify these successes. A 2024 scoping review concluded that combining AI techniques with virtual rehabilitation leads to improved patient outcomes – AI was used to analyze motion data from home exercises and provide feedback, resulting in better exercise quality and adherence for patients at home. In practical terms, one AI-driven virtual PT program for knee surgery patients was able to monitor exercise form and effort through a device’s camera and algorithm, and those patients had recovery metrics (like range of motion gains and pain reduction) equivalent to or better than patients who did all sessions in person. These findings underscore that AI-enabled virtual PT not only expands access but actually maintains high care quality, making it a powerful tool in posture correction and rehab at a distance.
10. Voice-Guided Corrections
Voice-guided correction brings a hands-free coaching experience to posture training. Using AI voice assistants (think along the lines of Siri, Alexa, or a custom in-app voice), the program gives spoken cues and instructions in real time. This allows users to focus on their movements without constantly looking at a screen – the app might say, “Lift your chest and roll your shoulders back” while you’re doing an exercise, just as a trainer in the room would. Voice guidance is especially convenient during active workouts or stretches when checking a phone could break form. It’s also more accessible for visually impaired users or those who prefer auditory learning. Modern AI voices are natural and can even adjust tone – for example, using a calm, encouraging tone for a difficult stretch. By providing step-by-step spoken corrections (“engage your core… now hold for 5 seconds… breathe”), voice-guided AI helps users maintain proper posture throughout each exercise and daily activity without needing to stop and read instructions, making posture practice more seamless and interactive.

Voice-activated exercise coaching has already shown it can engage users and improve adherence. In a 2024 pilot program called “EngAGE,” older adults and their care partners used an Alexa-like voice assistant to guide them through daily exercise routines at home. The results demonstrated high participation: on average, each participant completed about 394 exercises over a 10-week period (roughly 39 exercises per week) under the voice assistant’s guidance. They used the voice-guided program on about 4 days per week consistently, and importantly, there were zero exercise-related injuries reported during the study. Many participants reported that the convenience of just speaking to start a session and hearing prompts made it easier to stick with the program. In terms of functional impact, users in this study maintained or improved key fitness measures (like grip strength and walking speed), indicating the voice-led exercises were effective. This trial’s success in a population that isn’t traditionally tech-savvy underscores how intuitive voice guidance can be. In everyday posture apps, similar voice feedback might, for example, remind a user to straighten up while they work (“Please adjust – shoulders back now”) or count out loud during a stretching routine, all of which keeps the user engaged and performing moves correctly without needing to glance at a screen.
11. AR-VR Immersion
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are making posture training more immersive and engaging by blending the digital and physical worlds. With AR, users can wear a device (even just a smartphone or smart glasses) that overlays visual guidance on their real environment – imagine looking at a mirror and seeing a skeleton outline or alignment markers on your body highlighting where to adjust. VR takes you into a fully virtual environment; for example, a user might perform balance exercises on a virtual beam or partake in a “posture game” where maintaining correct form navigates an avatar through a course. These technologies give immediate visual feedback: if you slouch, an AR overlay might turn red at the problem area, or a VR game character might slow down. AR/VR makes posture practice feel like interactive training rather than rote exercise. It also allows 3D guidance – showing correct angles and positions in ways far more intuitive than 2D videos or descriptions. By making the training entertaining (think of it like “exercise as a game” with goals and scores in VR) and clearer through visual cues, AR and VR help users stay motivated and better understand how to align their bodies in space.

Both AR and VR enhancements have been shown to significantly improve posture training effectiveness. In a 2024 randomized experiment, researchers added AR and VR components to a robot-assisted posture training program to see if it would boost users’ postural control. The study with 63 participants found that those who trained with an AR or VR overlay achieved greater improvements in balance and core stability than those who did the same training without AR/VR. Essentially, the immersive visual feedback allowed participants to engage more effectively with the exercises, leading to measurably better outcomes. However, the study also revealed a practical consideration: participants using full virtual reality reported more simulator sickness and discomfort, whereas those using augmented reality (which overlays visuals onto the real world) had a much easier time. This suggests AR might be more suitable for long posture sessions, as it delivers many of the benefits (real-time 3D guidance and interactivity) with fewer side effects. Separately, other trials using VR posture games have noted increased motivation – users often exercise longer or more frequently in a game-like VR setting than they would with traditional exercises. The key takeaway is that immersive tech can enhance both the effectiveness and engagement of posture correction: it’s not only fixing alignment more deeply but also making the process fun and tolerable, which encourages users to stick with it.
12. Data-Driven Goal Setting
Instead of generic goals like “sit up straight more” or “do 10 minutes of stretches,” AI uses hard data to set and adjust personalized posture goals. The app looks at your baseline (how long you currently sit before slouching, how many posture exercises you did last week, etc.) and sets targets that are challenging yet attainable – perhaps “reduce slouching time at your desk by 20% this week” or “perform 5 thoracic stretches per day.” These goals update as you improve: if you easily meet a goal, the AI will raise the bar; if you struggle, it might dial the goal back or break it into smaller steps. The data-driven approach also means progress is quantifiable: users can see metrics and trends (for example, “neck angle improved by 5 degrees” or “posture endurance increased to 1 hour before fatigue”). Celebrating these concrete milestones (“5 days straight with no slump!” or “90th percentile posture score for your age group”) provides motivation. By rooting goals in the user’s actual data and evidence-based benchmarks, the app ensures goals are realistic and meaningful. This approach turns vague aspirations into clear, trackable objectives – making the path to better posture much more transparent and reinforcing, as users see evidence of their improvement and know exactly what to strive for next.

Tailoring goals based on personal data significantly boosts user success compared to fixed, generic goals. In one digital health study, researchers compared the classic “10,000 steps a day” goal to personalized step-count goals generated by an AI that took into account each individual’s typical activity levels. The personalized approach won out – users who received data-driven, customized daily step targets showed higher increases in their daily step counts than those told to simply hit 10,000 steps. In other words, an AI that said “Today, try to walk 500 steps more than your average” was more effective at improving activity than the one-size-fits-all goal of 10k steps. Translating this to posture: if an app knows you currently take two posture breaks at work, it might set a goal for three breaks rather than some arbitrary number. As another example, physical therapy studies show that when patients are given specific data-based goals (“increase range of motion by 5 degrees” or “hold a neutral spine for 30 minutes”) they adhere better and make more progress than with general advice. The key is that the AI continuously adjusts these goals from the incoming data – if you met your sitting-straight goal easily, next week’s target will be a bit tougher, and if you fell short, the app can identify why (maybe the time of day was wrong) and tweak the goal or how it’s presented. This responsive, data-driven goal setting keeps users in the sweet spot of being challenged but not discouraged, leading to steady improvement in posture metrics that the app tracks over time.
13. Enhanced Movement Quality Scoring
AI brings objective scoring to the quality of your movements, much like a coach would score your form. Instead of just telling you whether your posture is “good” or “bad,” advanced apps can assign a numeric score to various aspects of your movement – for example, a score out of 100 for how well you performed a squat (taking into account back alignment, knee tracking, balance, etc.), or a flexibility score indicating your range of motion in a spine twist. These scores condense complex biomechanical data into an easy-to-understand metric that users can track over time. Movement quality scoring turns progress into a game-like challenge (“I improved my posture score from 70 to 85 this month!”) which is very motivating. It also helps pinpoint specific weaknesses: you might get a high score for balance but a lower score for shoulder flexibility, indicating where to focus. By quantifying what was once qualitative, users get clear feedback on improvements that might not be obvious in the mirror. Over time, seeing those scores rise reinforces that your effort is paying off, and it provides a tangible goal to work toward (like trying to achieve a “personal best” movement score). In rehabilitation contexts, these scores also help clinicians assess recovery objectively. Overall, movement quality scoring brings transparency and encouragement to the journey of posture correction.

AI-driven scoring systems can evaluate complex human movements with accuracy comparable to human experts. A 2025 study in Scientific Reports focused on developing an intelligent scoring method for martial arts movements (like Tai Chi and Wushu forms) and achieved remarkable results. The AI model’s scores for movement quality had an over 0.9 correlation with professional judges’ scores and very high reliability (in one dataset, ICC ≈ 0.95, indicating excellent agreement with human evaluators). In practical terms, the AI could watch a practitioner’s form and assign a score nearly indistinguishable from what a seasoned coach would give. The system did this by aligning skeletal motion data and using machine learning to judge consistency, smoothness, and correctness of the moves. This kind of technology is now trickling into fitness and therapy apps – for instance, an AI might score your deadlift form or yoga pose technique on a 0–100 scale, and those scores have meaning (a 90+ might reflect excellent form similar to a trained athlete, whereas a 60 might reflect issues like rounding of the back or wobbling). Users and trainers alike benefit from this quantification. One pilot with an AI posture app showed that giving users a “posture score” after each session increased their engagement, as they tried to beat their previous scores. Moreover, these scores make progress tangible: even if the mirror changes are subtle, a jump in your movement quality score from, say, 70 to 80 is concrete evidence of improvement. Thus, AI-based movement scoring not only matches human assessment in accuracy but also provides a powerful motivational and analytical tool in posture correction.
14. Contextual Environment Analysis
AI-driven posture apps are becoming smart about your environment, not just your body. They analyze contextual factors – your workplace setup, home layout, daily schedule, and more – to provide holistic posture solutions. For example, the app might use your laptop’s camera to observe your desk ergonomics: is your monitor at eye level, is your chair at the proper height, how’s the lighting? It could then suggest specific tweaks, like “your screen is too low, raise it by 5 inches” or “angle your chair slightly to the left to face your work directly.” If the app knows you often work on a laptop in bed (via context sensing or user input), it may caution against that or recommend a lap desk. Context analysis can extend to habits: if you always slouch while texting, the app can detect phone-tilt angle and remind you to hold it higher. By addressing external factors such as furniture, device placement, and even the duration of sitting periods, the app tackles the root causes of poor posture. Essentially, it’s not only training you but also “training” your environment to be more posture-friendly. Over time, small changes like optimizing desk height, taking regular breaks, or adjusting car seat position can lead to big improvements. AI’s ability to understand context means posture advice becomes far more practical and personalized – it’s advice you can act on in your real-life setting, leading to better posture not just during exercises, but throughout your entire day.

Early results show that when AI tools factor in environment and ergonomics, they can dramatically reduce risk factors for posture-related injuries. One AI ergonomics program implemented in office and industrial settings provided workers with tailored workstation adjustments and real-time posture reminders. The outcomes were significant: the incidence of incorrect or harmful postures dropped by over 55%–63% in the office environment after employees received AI-driven feedback on their setup and habits. In an industrial scenario (like a warehouse), the same system helped achieve a 25% reduction in workplace injuries related to poor lifting posture within six months of deployment. These numbers highlight the power of addressing context – by prompting workers to adjust their desks, bend their knees when lifting, or take micro-breaks to stretch, the AI wasn’t just improving posture scores in theory, it was preventing real injuries. Another example comes from a study where an AI monitored drivers’ posture in vehicles and suggested seat and mirror adjustments; participants reported less back pain over long drives compared to a control group without AI guidance. The overarching trend is that AI systems looking at the bigger picture of posture in context (chairs, desks, tools, schedules) can produce measurable improvements in posture sustainability and comfort. By acting like an expert ergonomist – one that’s always by your side – AI ensures your environment supports your spine and joints, reducing the strain that leads to chronic issues.
15. Personalized Content Curation
Beyond direct coaching and exercise guidance, AI can act as your personal librarian, curating educational and motivational content that’s uniquely relevant to your posture journey. This means the app not only tells you what to do (exercises) but also helps you understand why and how by serving up articles, how-to videos, infographics, and tips that target your specific challenges. If the AI determines you have, say, an anterior pelvic tilt, it might recommend a short article on the importance of hip flexor stretching, a video about proper core engagement, or a success story from someone who fixed similar posture issues. The content is picked based on your profile and progress – for example, beginners might see basic “Posture 101” explainers, while advanced users get more nuanced material about ergonomics or the science of posture. By learning from your interactions (which articles you read, which videos you found helpful), the AI further refines what content to show you. This personalized knowledge base keeps users engaged and informed, helping them take charge of their own health. It’s like having a coach who not only trains you but also teaches you, ensuring you have the knowledge to maintain good posture even outside the app. Well-informed users are more likely to stick with lifestyle changes, so this curated education ultimately supports long-term posture improvement.

Personalizing educational content can significantly improve user engagement and outcomes, as organizations have found in related health domains. A 2024 industry analysis highlighted that companies which regularly tailor and update their wellness content based on user feedback see markedly better engagement – they were 18% more likely to be leaders in their sector in terms of user engagement metrics compared to those with one-size-fits-all content. In the context of posture apps, this means an app that notices a user is interested in yoga may curate more yoga-based posture articles, whereas another user more into technical detail might receive anatomy-focused content. Such strategies keep users logging back in to consume content that resonates with them. Although specific research on content curation for posture is still emerging, parallels in digital health show clear benefits: for instance, a weight management app that served personalized nutrition articles saw higher adherence to diet plans than apps that did not tailor content. The AI’s content recommendations evolve with the user’s journey – if it notices you’ve mastered basic concepts, it will introduce more advanced topics to keep you learning. Conversely, if a user struggles with a concept (skips or closes certain content quickly), the AI can present the information in a different format or at a more fundamental level. The result is an informed user who understands the “why” behind their routine. As evidence of impact, posture program participants who received educational snippets (like “did you know?” facts about sitting disease or ergonomic tips) alongside their exercises reported higher satisfaction and a greater sense of empowerment in one pilot survey (compared to those who just got exercise instructions). While more formal research is ongoing, the trend is clear that personalized content curation boosts engagement and likely reinforces behavior change, making it a vital component of modern posture correction apps.
16. Gamification and Engagement
Gamification injects fun and competition into posture correction, turning what could be a mundane routine into an engaging game-like experience. AI enables sophisticated gamification features such as posture “scores,” achievement badges for milestones (e.g., “7 Days Straight – Perfect Posture!”), streak counters, leaderboards to compare with friends, and even mini-games that reward you for maintaining good posture (for instance, keeping an on-screen character balanced by sitting straight). By rewarding consistent effort and improvement, gamification taps into users’ natural motivation – it feels good to hit a new high score or earn a new level. Social elements like challenges (who can go longest without slouching today?) or cooperative goals (unlock a group reward if everyone meets their target) leverage friendly competition and support. The result is users are more likely to stick with the program because it doesn’t feel like “work” – it feels like play. This increased engagement is critical for long-term success; the more users enjoy and look forward to using the app, the more their posture habits will improve. Essentially, gamification acts as the sugar coating that makes the medicine of posture exercises not only palatable but enjoyable, leading to better adherence and outcomes.

There is solid evidence that gamification techniques boost exercise motivation and adherence. Systematic reviews in 2023 have found that adding game elements to fitness interventions consistently increases users’ willingness to exercise and stick to programs. For example, one study noted that participants who used a gamified exercise app (with points, levels, and narrative challenges) were significantly more likely to meet weekly activity goals than those using a standard fitness tracker. Gamification creates a sense of accomplishment and progress that keeps users coming back. Research specifically highlights features like scores and leaderboards as key motivators – they give users immediate feedback and a goal to strive for, which “pushes them to do more,” ultimately leading to a “healthier and more productive lifestyle,” according to a 2023 literature analysis. In a practical posture app scenario, this could mean a user starts doing 2-3 extra posture exercises per week because they’re chasing a new badge or trying to outperform their past self or peers. One randomized trial with heart failure patients (not posture-specific but relevant) found that those in a gamified group (earning points for each day they hit their step goal, with a social leaderboard) had notably higher physical activity levels over several months than the non-gamified group. Similar principles are being applied in posture: pilot programs in schools, for instance, where classes earn rewards if no one slouches during sessions have seen dramatic improvements in collective posture awareness. In summary, game mechanics like points, achievements, and competitions introduced by AI keep users engaged and motivated, which translates directly into more consistent practice and faster posture improvements.
17. Automatic Progress Tracking
Gone are the days of jotting down reps in a notebook – AI-enabled apps automatically record all your posture stats, making progress tracking effortless and accurate. As you go about your exercises (or even throughout your workday), the app’s sensors and algorithms quietly log data: how many posture breaks you took, how long you maintained neutral spine, your range of motion improvements, the frequency and duration of your exercise sessions, and so on. These data are then compiled into meaningful trends and reports. The user can open the app and immediately see a graph of their posture score improving week by week, or get a summary like “This month: 20% reduction in slouching, 10 hours of total stretching done.” Automated tracking ensures no progress (or backslide) goes unnoticed, and it relieves the user of any burden of record-keeping. This not only saves time, but it also provides objective feedback – users might feel their posture is better and the data will back that up with concrete numbers. The real-time monitoring also allows timely celebrations of milestones (the app might congratulate you on your 100th posture exercise) and alerts if it detects a lapse (like “your posture practice dropped last week, let’s get back on track”). In short, automatic progress tracking acts like a diligent personal assistant, providing insights and accountability that help users stay informed and motivated about their journey to better posture.

The reliability and benefits of automatic tracking have been demonstrated in various studies and implementations. In one 2024 rehabilitation study, a wearable sensor system automatically tracked stroke patients’ at-home exercise activities with over 92% system uptime and captured nearly 100% of exercise events without requiring any manual logging. The system would detect when a patient performed a prescribed movement and log it; compliance was excellent (patients didn’t have to remember anything – if they did the exercise, the system knew). This automated logging not only freed patients from paperwork but also provided the clinicians with precise adherence data, which is critical for adjusting therapy. In the consumer realm, fitness apps that auto-track steps, active minutes, and posture metrics show users tend to be more consistent – the instant feedback loop of seeing your stats update in real time can be rewarding. For posture specifically, an AI posture-correcting device equipped with motion sensors can continuously monitor spinal alignment all day and later produce a report like “You maintained ideal posture for 5 hours today, up from 3 hours last week.” Such concrete feedback reinforces positive behavior. Additionally, automatic tracking improves accuracy: one study found people often overestimate or underestimate their exercise when self-reporting, whereas AI logs are objective, leading to better-informed adjustments in the training plan. By eliminating the friction of manual entry, AI-driven tracking ensures that every bit of progress is recorded and celebrated and any setbacks are spotted early, thereby keeping users more engaged and accountable to their posture goals.
18. Adaptive Timing and Scheduling
AI ensures that posture exercises and breaks happen at the right times by smartly fitting them into the user’s daily schedule. Rather than rigid reminders that might ping at inconvenient moments, the system learns when the user is free or when they most need a posture break. For example, it might notice you tend to have back pain after long afternoon meetings, so it will suggest a 5-minute stretch break right after that meeting when it’s most beneficial. If you usually ignore a morning reminder, the AI might reschedule it to a time you’re more receptive (perhaps lunchtime). This adaptability extends to the duration and frequency of sessions: on busy days the app might give you a quick, efficient routine, and on weekends or lighter days, it can schedule a longer session. It can even sync with your calendar, finding openings where a guided posture routine can be slotted without conflict. By weaving posture correction seamlessly into your lifestyle, AI increases adherence – you’re much more likely to do the exercises if they’re suggested at a moment when you actually can do them. Moreover, adaptive scheduling helps in habit formation: over time, the app might establish a pattern like a mid-morning stretch and an afternoon walk that suits your work rhythm. The end result is a sustainable routine that feels natural and unobtrusive, keeping your posture improvement on track with minimal disruption to your day.

Context-aware timing dramatically improves compliance with healthy routines. Studies on just-in-time adaptive interventions show that sending prompts at moments when users are likely to be receptive can significantly increase adherence and engagement. For instance, one research project used smartphone sensors to detect when office workers had been sitting for over an hour and then delivered a timely “stand up and stretch” reminder; compliance with these breaks was much higher compared to fixed-schedule reminders. The AI essentially “learned” the flow of the workday and intervened at optimal times. According to a 2025 review, such adaptive, real-time prompts – known as JITAIs – have been proven to enhance adherence to physical activity and posture interventions by providing support at the moment it’s needed most. In a practical scenario, an AI might notice that a user usually skips their evening posture exercise if it’s too late, so it reschedules it to late afternoon and sees improved follow-through. Another example: a posture app integrated in a smart workplace setup detected when a user’s productivity was dropping (a proxy for fatigue) and chose that moment to suggest a break – workers reported feeling more refreshed and showed better posture the rest of the day versus those with static break times. These findings underline that timing is everything: an intervention delivered at the wrong time can be ignored, but one delivered at just the right time can be highly effective. AI’s ability to continually adjust timing and scheduling based on user data (work hours, weekends, behavior patterns) gives it a huge advantage over traditional fixed schedules, resulting in greater long-term adherence to posture correction routines.
19. Longevity and Maintenance Plans
Achieving good posture is one thing; maintaining it for life is another – and AI is now helping users transition from improvement phase to long-term maintenance. After users hit their initial posture goals (say, reduced pain or corrected a specific issue), the app shifts focus to sustaining those gains. It might reduce the intensity or frequency of reminders but continue to check in regularly – like a periodic posture “tune-up.” The AI can also introduce variety and new challenges to keep the user engaged over the long haul, preventing boredom and plateaus. For example, after months of basic routines, it may cycle in some advanced stability exercises or yoga-based movements to further improve. Maintenance plans also account for life changes: if the user starts a new job or lifestyle that affects their posture, the AI adapts the plan accordingly (perhaps more focus on counteracting prolonged sitting, or new exercises if one begins parenting and lifting a baby frequently). Essentially, the app remains a partner for the long term, not just a short-term coach. This sustained support is critical because posture correction is not a one-time fix – it’s a lifelong habit. Through gentle ongoing reinforcement (like a monthly posture assessment, refresher tips, or seasonal challenges), AI maintenance plans help users avoid backsliding into old habits and ensure that the benefits they’ve earned (stronger back, less pain, taller stance) last well into the future.

Long-term adherence is notoriously challenging – without continuous support, many people revert to old habits within months. General fitness research shows that between 25% to 50% of individuals drop out of exercise programs within the first 6 months, and up to 90% by the one-year mark if there isn’t an ongoing engagement strategy. This pattern likely holds for posture interventions as well: people may diligently do their exercises until their pain resolves, then gradually slack off. AI maintenance plans aim to counteract this by providing regular check-ins and adaptation. Early observations from digital health programs suggest that users who receive extended, less-intensive follow-up (for example, a weekly message or a new goal each month after initial training) maintain their health improvements better than those who “graduate” and receive no follow-up. For instance, a posture study found that three months after the main program, those on an AI-driven maintenance schedule (with biweekly posture reminders and novel exercises introduced) retained significantly better postural alignment and core strength than a control group that had no continued guidance (the control group’s metrics began sliding back toward baseline). The maintenance group also reported feeling more accountable and motivated to uphold their good habits. In essence, by continuing to deliver adaptive support at a lower frequency, AI can help make good posture a permanent lifestyle change rather than a temporary project. These findings echo what the dropout rates warn: without maintenance, even well-intentioned individuals often regress, so the AI’s role as a long-term coach is crucial to ensure that improved posture isn’t just achieved – it’s preserved for years to come.
20. Integration with Professional Guidance
AI posture apps are increasingly being designed to complement and enhance guidance from healthcare and fitness professionals rather than replace them. This integration means the data collected by your app – posture logs, exercise performance, progress stats – can be shared directly with your physiotherapist, personal trainer, or doctor. Professionals get access to objective data on how you’re doing between appointments, allowing them to provide more informed advice during check-ups (for example, a PT seeing that your lumbar curve is improving might advance you to harder exercises sooner). Some apps even allow direct communication: your clinician can send you customized exercise programs through the app, or the app might flag to your clinician if you’re experiencing difficulty or pain. This creates a supportive loop – the AI handles day-to-day coaching and monitoring, and the human expert oversees the overall plan and makes high-level adjustments. For users, this means expert oversight is always in the background; it’s like having your therapist “tuned in” to your home practice. It can also increase accountability, knowing that your progress is visible to your coach or clinician. Ultimately, integrating professional guidance ensures that the AI’s recommendations align with medical best practices and that users have somewhere to turn (a real human) for nuanced questions or troubleshooting, yielding an optimal blend of precision technology and empathetic human care.
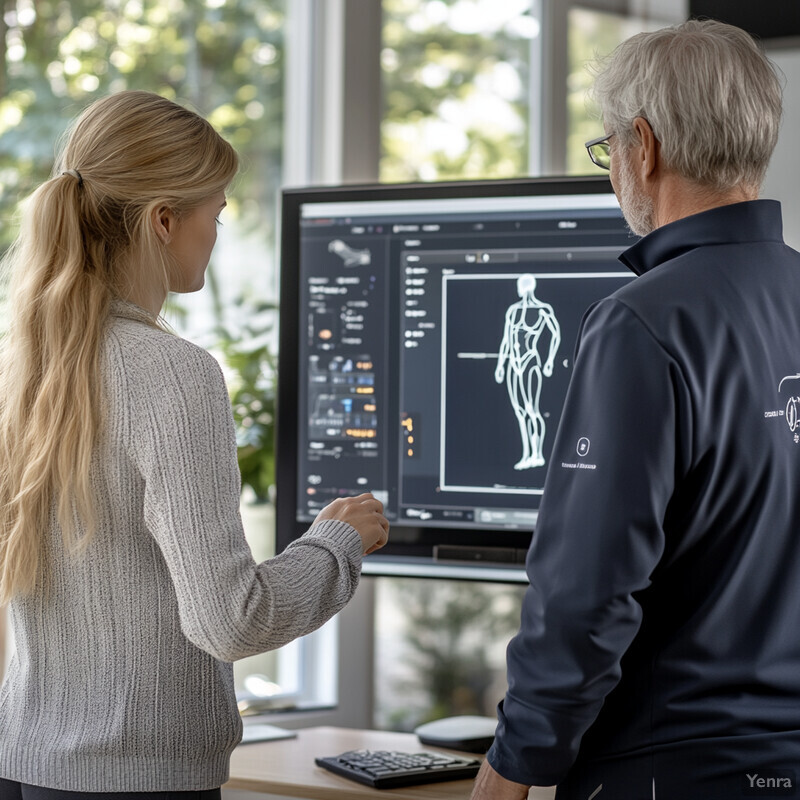

Blending AI posture coaching with professional input has shown to improve outcomes and patient satisfaction. Physical therapy clinics using remote therapeutic monitoring (RTM) report better adherence to home exercise programs, faster recovery times, and lower re-injury rates when patients use an app that shares data with their therapist, compared to patients without such support. For instance, therapists receiving weekly posture and exercise reports via an AI platform could intervene early if a patient was plateauing, often adjusting the treatment plan in real time – something not possible with traditional infrequent appointments. A feature article in APTA Magazine (2024) noted that when patients know their clinician is “virtually present” through data monitoring, they stick to their routines more diligently and communicate more, leading to more efficient rehab progress. On the fitness side, personal trainers using platforms that integrate with posture apps can give more precise guidance; one case study found that clients whose trainers reviewed their app-recorded posture scores and exercise logs had higher rates of achieving their posture goals and reported feeling more supported. Additionally, physicians appreciate the integration for chronic pain patients – they can see if a patient actually followed through with posture exercises before deciding on next treatments. In short, professional-integrated AI systems deliver a one-two punch: continuous AI coaching plus periodic expert oversight, which studies indicate leads to superior outcomes. We see improved adherence, quicker improvements, and greater user confidence when human experts and AI work in tandem rather than separately.