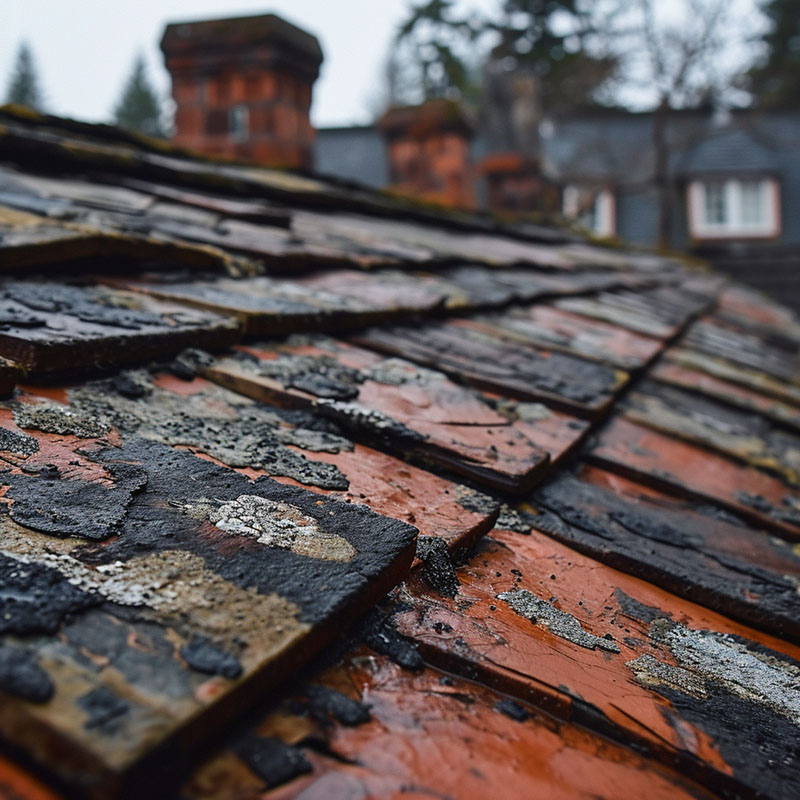
Acid Rain Damage on Roofing

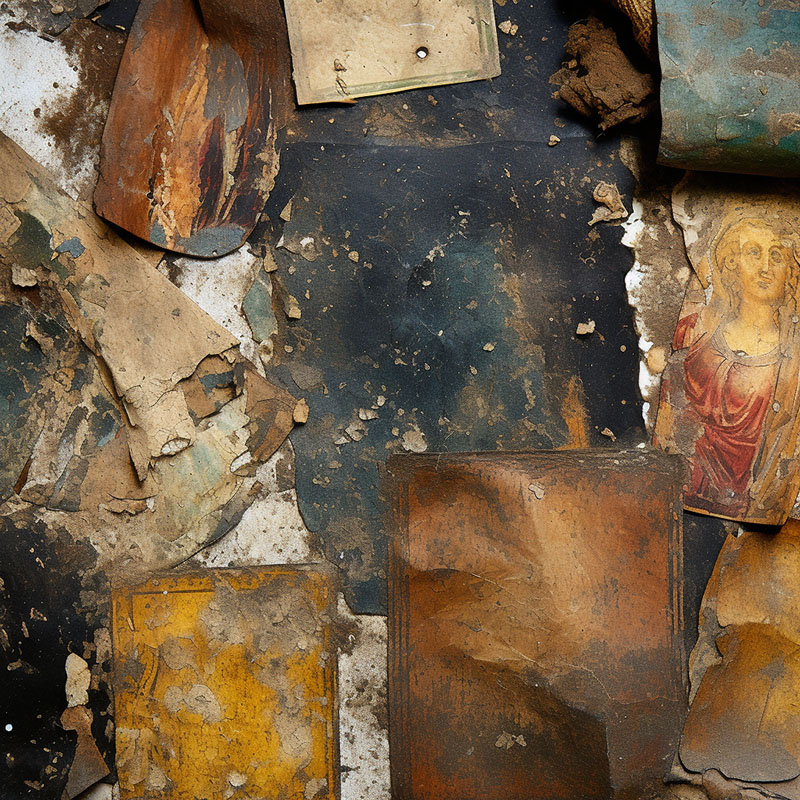
Acid Rain Impact on Historical Artifacts

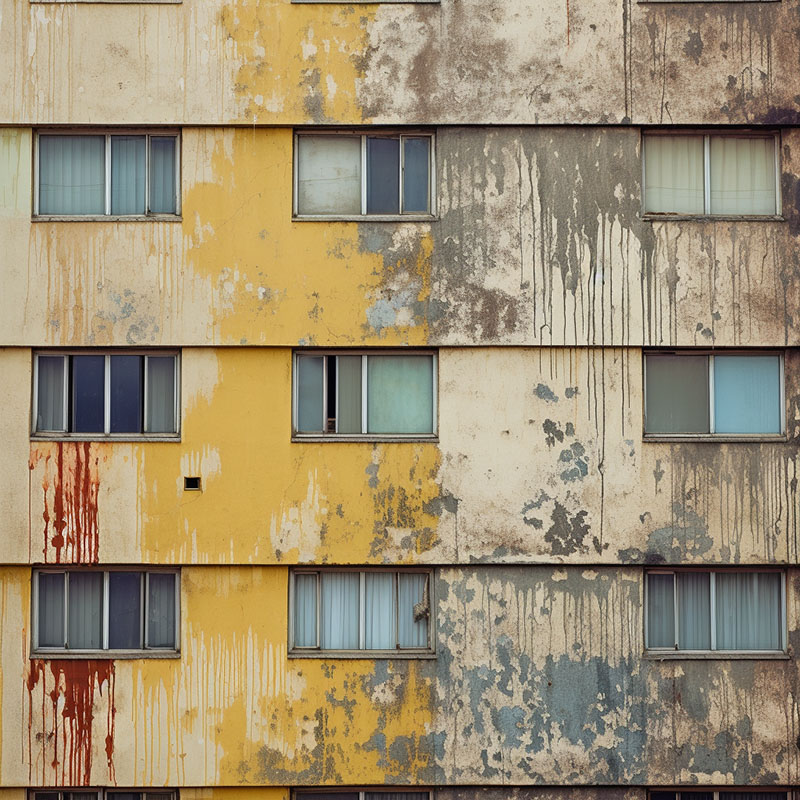
Acid Rain Stains on Buildings

Acid Rain Damage on Statues
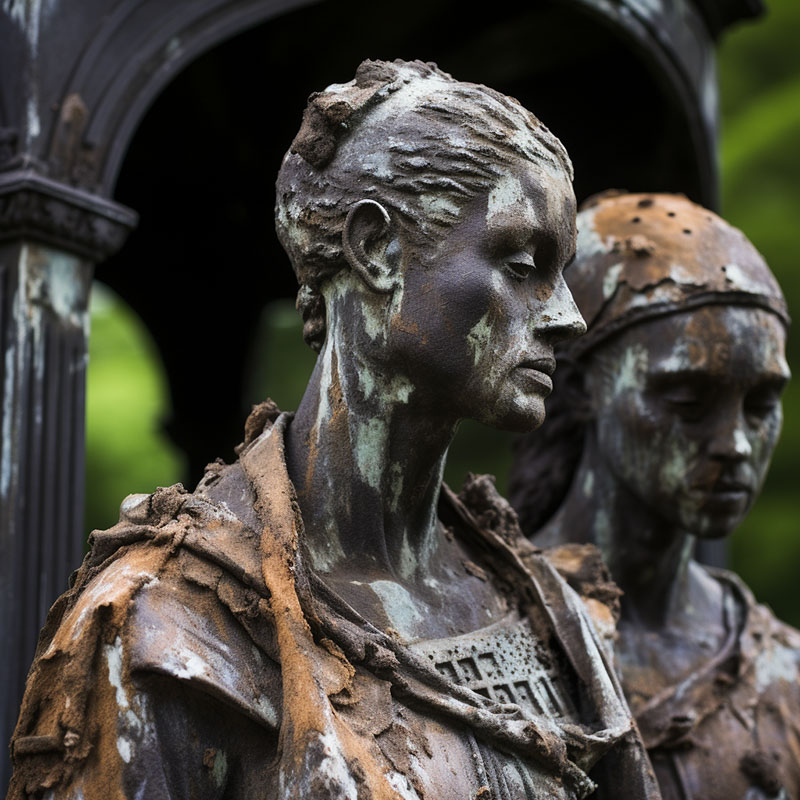
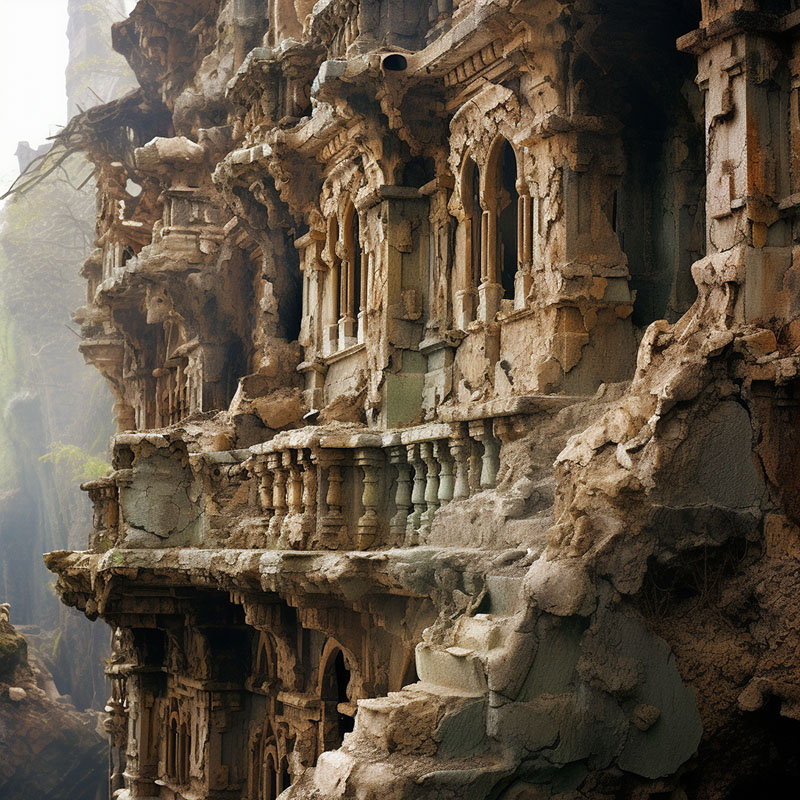
Erosion of Historical Architecture

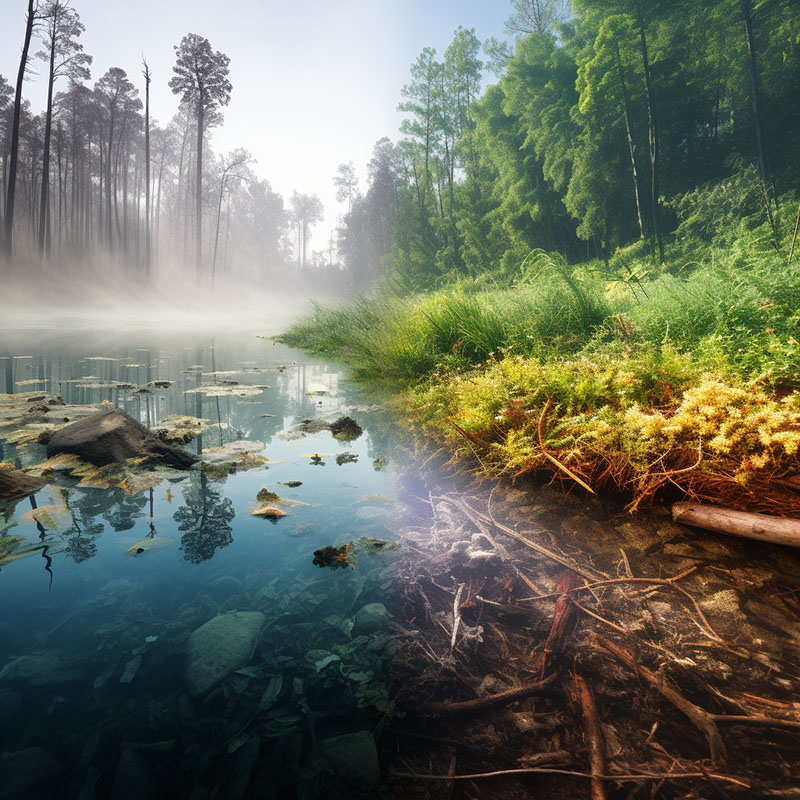
Comparison of Healthy vs Acid Rain-Affected Environment

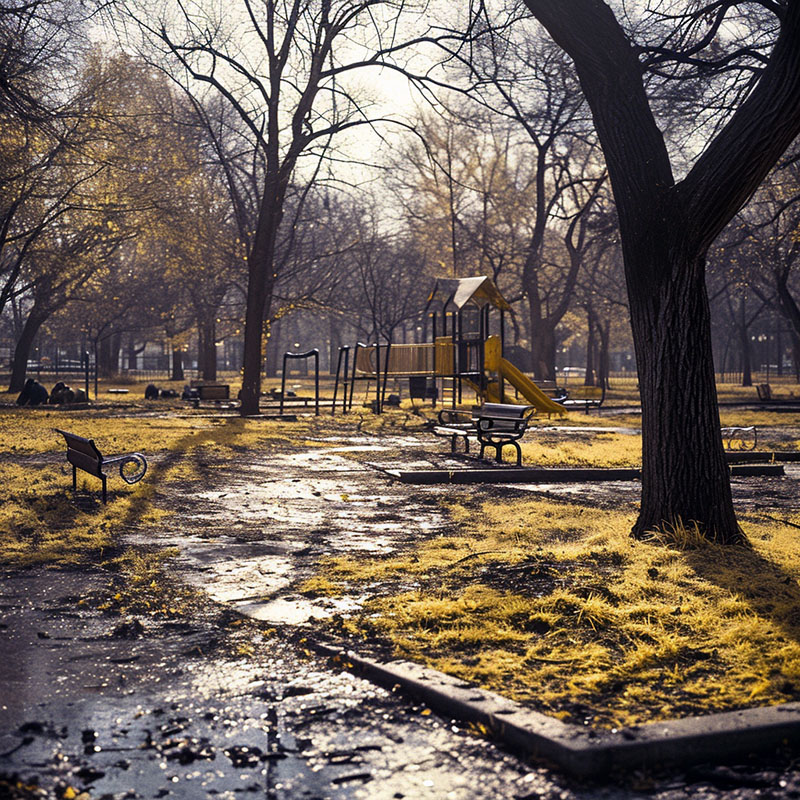
City Park Affected by Acid Rain

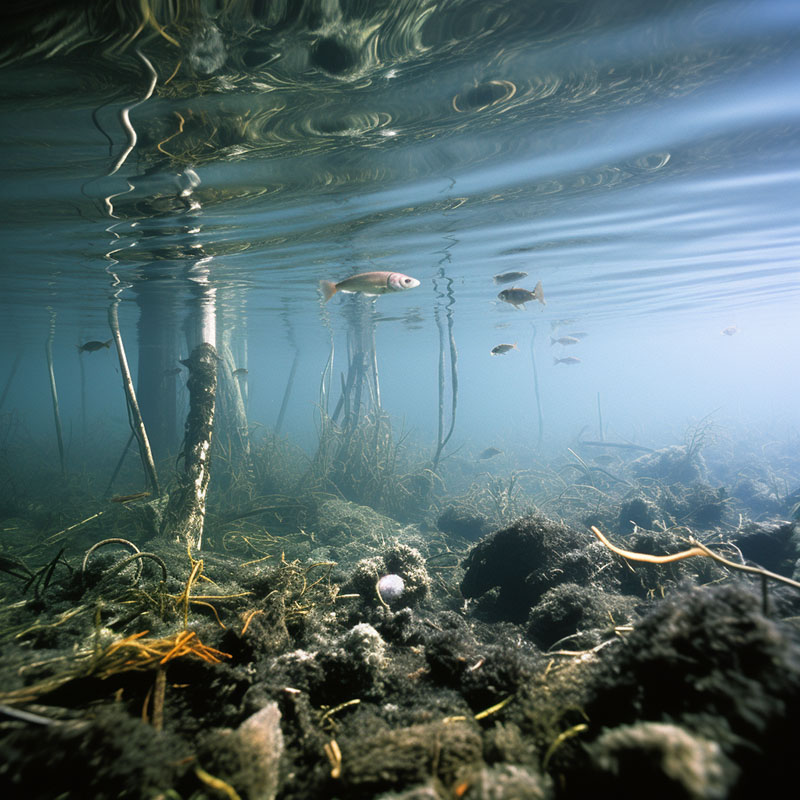
Acid Rain Impact on Aquatic Life

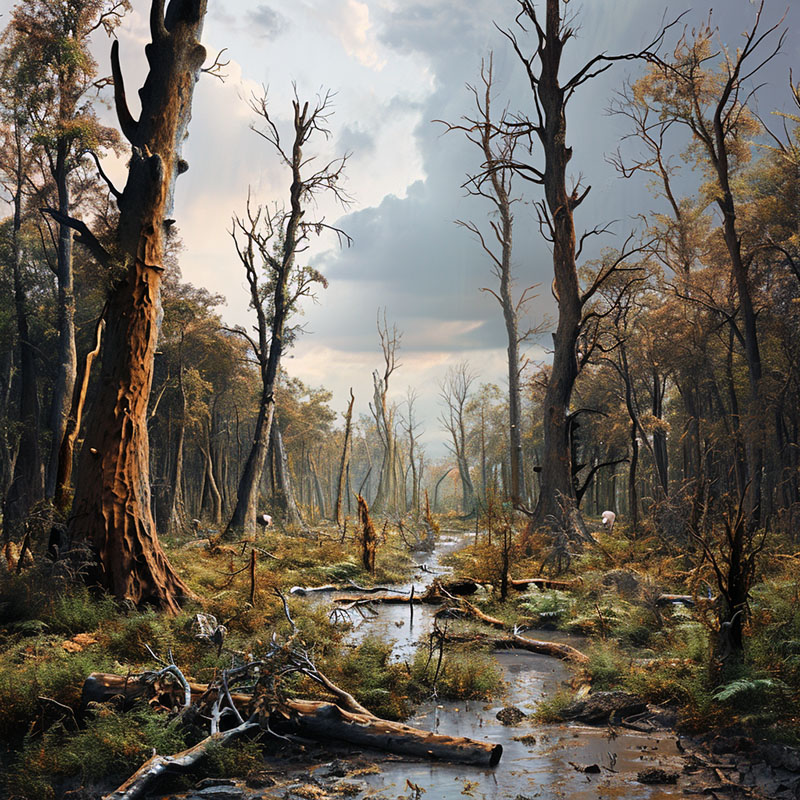
Forest Damaged by Acid Rain


Frozen Acid Rain On Europa?
Frozen sulfuric acid on Jupiter's moon Europa is depicted in this image produced from data gathered by NASA's Galileo spacecraft. The brightest areas, where the yellow is most intense, represent regions of high frozen sulfuric acid concentration. Sulfuric acid is found in battery acid and in Earth's acid rain. This image is based on data gathered by Galileo's near infrared mapping spectrometer. Europa's leading hemisphere is toward the bottom right, and there are enhanced concentrations of sulfuric acid in the trailing side of Europa (the upper left side of the image). This is the face of Europa that is struck by sulfur ions coming from Jupiter's innermost moon, Io. The long, narrow features that crisscross Europa also show sulfuric acid that may be from sulfurous material extruded in cracks. Image Credit: NASA/JPL.
Acid Rain Eroding a Statue
 Over time, statues are being eroded by acid rain. This angel seems to show the sadness of this happening.
Over time, statues are being eroded by acid rain. This angel seems to show the sadness of this happening.
Acid Rain Decreasing in Northeast
February 11, 2002 - Signs of Recovery in Adirondack Lakes Apparent, Say Researchers at Rensselaer's Darrin Fresh Water Institute
Over the years acid deposition, commonly referred to as "acid rain," has rendered dozens of lakes in the Adirondacks uninhabitable for fish and other wildlife. Now, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute researchers at the Darrin Fresh Water Institute (DFWI) have indicated that some of the most severely affected lakes in that region are showing signs of recovery.
"In about half of the 30 lakes under study, an increase in the pH has been observed, a sign that acidic levels are decreasing," says Director Sandra Nierzwicki-Bauer.
Levels of nitrogen influenced by nitric oxide, a primary source of acid rain, have decreased moderately in 18 of the 30 lakes the DFWI has monitored since 1994 through its federally funded Adirondack Effects Assessment Program. There also has been an overall reduction of sulfuric acid, another main contributor of acid rain that comes from industry pollutants.
The reductions may be correlated with the 1990 Clean Air Act, a federal mandate to significantly reduce emissions that cause acidification, says Nierzwicki-Bauer.
More research is needed to pinpoint the exact reasons for the apparent changes seen in the lakes in the southwestern part of the Adirondack Park, an area hardest hit by acid rain.
"Recovery doesn't happen overnight," says Charles Boylen, professor of biology and DFWI associate director. "One of the reasons we need long-term data is that other factors can come into play. More or less rainfall in a year, for instance, can lead to a temporary shift in acid-rain levels. You need to track specific data over 10 to 15 years."
The DFWI's long-term strategy recently has led to a $2.36 million grant from the Environmental Protection Agency. The five-year grant will allow the DFWI and its collaborators to study acid rain effects in four more lakes in addition to monitoring the other 30. During a workshop in June at the Institute, researchers will announce the most up-to-date results in the acid-rain studies to leading scientists around the country.
The Darrin Fresh Water Institute, established more than 25 years ago, has helped increase public awareness concerning the protection of land, water and air. The Institute's all-encompassing study of fresh water systems and ecological processes has earned it high regard in the national scientific community and high marks from the general public.
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, founded in 1824, is the nation's oldest technological university. The school offers degrees in engineering, the sciences, information technology, architecture, management, and the humanities and social sciences. Institute programs serve undergraduates, graduate students, and working professionals around the world. Rensselaer faculty are known for pre-eminence in research conducted in a wide range of research centers that are characterized by strong industry partnerships. The Institute is especially well known for its success in the transfer of technology from the laboratory to the marketplace so that new discoveries and inventions benefit human life, protect the environment, and strengthen economic development.