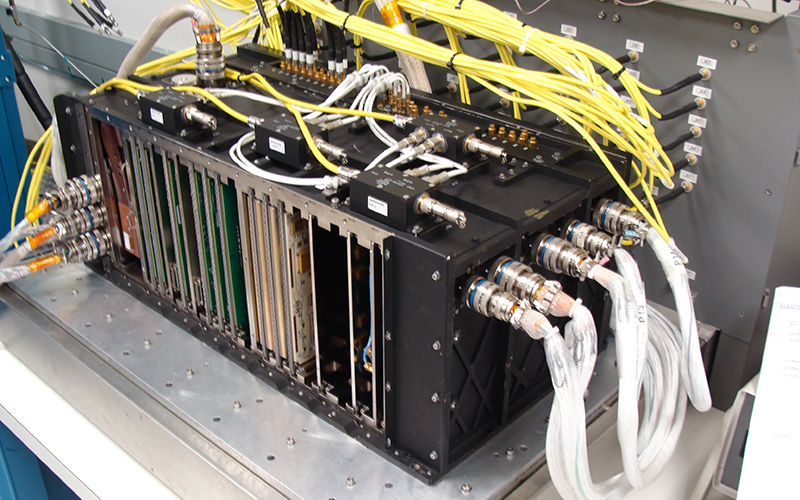
Announced November 8, 2017, Harris Corporation has completed development of the company's fully digital Mission Data Unit (MDU), which is at the heart of its navigation payload for Lockheed Martin's GPS III satellites 11 and beyond.
GPS Block IIIA, or GPS III is the next generation of GPS satellites, which will be used to keep the Navstar Global Positioning System operational. Lockheed Martin is the contractor for the design, development and production of the GPS III Non-Flight Satellite Testbed (GNST) and the first eight GPS III satellites.
The current Harris payload for GPS III space vehicles (SVs) 1-10 includes a greater than three times reduction in range error, up to eight times increase in anti-jamming power, added signals – including one compatible with other Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) – and greater signal integrity. Harris' GPS III SV11+ fully digital navigation payload will further improve on performance for the U.S. Air Force by providing more powerful signals, plus built-in flexibility to adapt to advances in GPS technology, as well as future changes in mission needs.
The payload design ensures flawless atomic clock operations, providing the reliable GPS signal that millions of people – including U.S. soldiers – and billions of dollars in commerce depend on every day. The digital mission data unit also will provide the clock signal for a new GPS III Search and Rescue (SAR) payload.
On May 5, 2016, the U.S. Air Force awarded three Phase One Production Readiness Feasibility Assessment contracts for GPS III Space Vehicles (SV's) 11+, one each to Boeing Network and Space Systems, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, and Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems.
Beyond flexibility and reliability, the new Harris SV11+ navigation payload offers a smooth transition to the Air Force's GPS OCX ground control segment. The Harris payload for the first ten GPS III satellites already has been verified for OCX compatibility, and this will allow Harris to seamlessly port the Harris SV11+ design, minimizing integration risks and associated costs.