1. Precise Body Scanning
AI-powered 3D body scanning generates an exact digital model of a customer’s physique, eliminating guesswork in sizing. This precise measurement enables more accurate fit suggestions and personalized clothing recommendations. By capturing detailed dimensions (e.g. shoulder width, torso length, limb circumference), scanning ensures clothes are tailored to the individual’s unique shape. These tools can significantly reduce size-related uncertainty, increasing customer confidence in purchasing. The enhanced fit accuracy helps lower return rates and waste, making shopping more convenient and sustainable. Overall, precise body scanning streamlines the fitting process by aligning real body data with garment measurements.
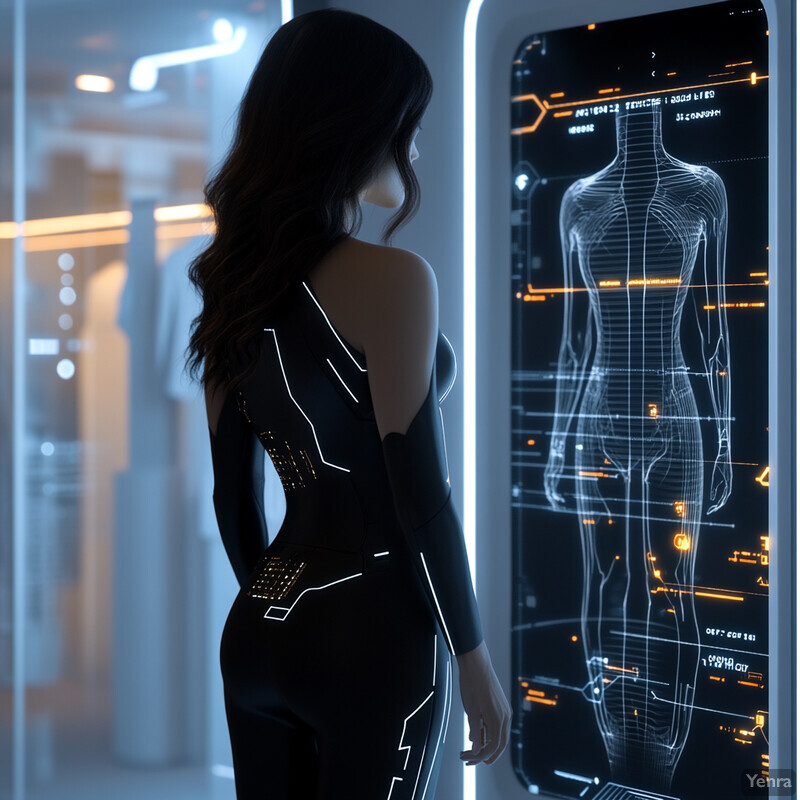

Recent studies confirm the accuracy and impact of 3D body scanning for apparel fitting. Research by Youn et al. (2023) notes that 3D body scanners “capture body images to produce accurate 3D models” used in apparel mass customization. In practice, retailers like Bloomingdale’s and New Look have piloted in-store scanning pods to match garments to customers’ body shapes. Industry data show fit issues cause over half of apparel returns, suggesting precise scanning could mitigate this major pain point. For example, Coresight Research and 3DLOOK report that when retailers implement AI-driven size-recommender tools, 80% see higher conversion rates. A 2023 case study from 3DLOOK demonstrated that a Scandinavian outerwear brand raised its production accuracy from 85.4% to 100% after adopting 3D body scanning, eliminating remakes and enabling confident online sales. In short, academic and industry sources show that accurate body scans create reliable fit data, directly addressing sizing returns and boosting sales.
2. Real-Time Fit Recommendations
Real-time fit recommendation systems use AI to instantly suggest the best size for a customer as they shop. By analyzing the scanned body model or entered measurements, the system compares them to each garment’s specifications. It then informs the shopper which size is most likely to fit well. This instant feedback eliminates uncertainty and speeds up decision-making. It can be offered via store kiosks, apps, or smart mirrors, often before the customer enters the dressing room. The overall effect is a personalized fitting experience that boosts shopper confidence. Ensuring customers immediately see which size should fit reduces frustration and the need to try multiple sizes.
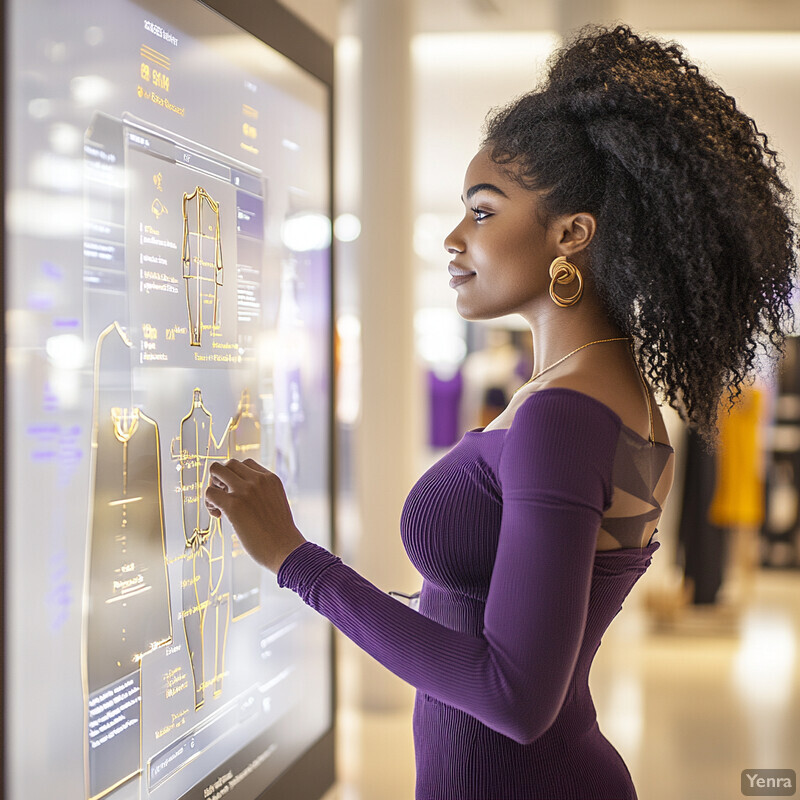

Industry reports highlight the effectiveness of AI-driven sizing suggestions. For instance, Amazon’s Chief Scientist of Shopping Technology explains that their deep-learning algorithm groups customers with similar fit preferences to recommend sizes. Amazon’s internal data show that when a specific size is recommended, customers are more likely to complete a purchase and less likely to return the item. In general, research confirms that size/fit issues drive roughly 53% of returns in online apparel, indicating ample room for AI solutions. Moreover, in the apparel market, 80% of retailers who have implemented AI-powered size-recommender tools report higher conversion rates. These figures suggest that making instant fit recommendations – a “real-time” algorithmic answer to “what size should I get?” – can significantly improve sales metrics and customer satisfaction.
3. Virtual Try-Ons
Virtual try-on technology leverages augmented reality to let customers “try on” garments digitally. Shoppers can see how clothes look on them by overlaying 3D garments on a live camera view or avatar. This removes the need for physical changes and provides a convenient, hygienic alternative. It also helps customers visualize items without having to undress or use communal fitting rooms. Virtual try-ons enhance the shopping experience by offering interactive previews and reducing uncertainty about fit and appearance. They cater to tech-savvy consumers and can be accessed via in-store kiosks, mobile apps, or online platforms. The net effect is higher engagement and confidence before purchase, especially important for e-commerce.
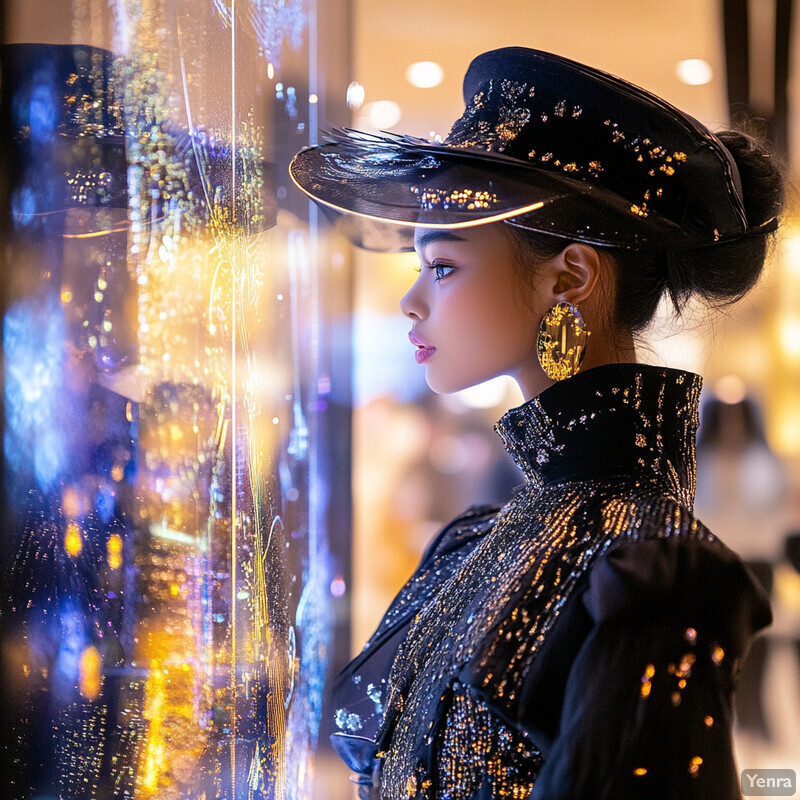

Recent market analyses indicate rapid growth and adoption of virtual fitting-room technologies. For example, a 2024 research report notes that the global virtual fitting room market was already valued at $6.6 billion in 2024, and is projected to reach $18.9 billion by 2030. These immersive solutions combine AR, AI and high-resolution sensors to provide realistic previews. Industry surveys also find that about 85% of apparel retailers use or plan to use AR/VR fitting tools. By integrating virtual try-ons, retailers can capture customers who prefer contactless experiences and reduce friction in online shopping. The technology’s popularity reflects retailers’ and consumers’ interest in minimizing returns: a McKinsey-style study shows that VR dressing rooms can reduce return rates by 20–30% in apparel by ensuring shoppers get a better sense of fit before buying. All together, market data and industry reports demonstrate that virtual try-ons are a growing channel, improving conversion and reducing fit-related returns.
4. Personalized Style Curation
AI-driven style curation goes beyond size – it tailors outfit suggestions to an individual’s taste. By analyzing purchase history, browsing behavior, and style preferences, these systems recommend outfits or pieces that match a shopper’s personal style. This can include entire “looks” with matching garments, color-coordinated items, or the customer’s favored cuts and brands. The result is a digital stylist or wardrobe consultant within the fitting room. Customers appreciate these customized recommendations because they discover new items they are likely to love, saving time on searching. Personalized curation can increase engagement and even the size of the transaction, as customers are presented with appealing choices aligned with their unique identity.

Data from industry and market research indicate that consumers and businesses see big value in personalization. A 2023 industry report notes that roughly 73% of consumers expect brands to understand their individual needs and offer personalized experiences. Practical implementations bear this out: AI-driven product recommendations have been observed to boost sales by 15–20% on average. For example, major online retailers like ASOS and Zalando attribute a significant portion of sales uplift to their AI recommendation engines. Moreover, in one case study, implementing “complete-the-look” style suggestions increased a retailer’s conversion and cross-sell rates by 30–40%. This evidence shows that a fitting room which curates outfits to a shopper’s style – by learning what they prefer – can appreciably improve customer satisfaction and revenue.
5. Voice-Activated Assistance
Voice-activated systems allow shoppers to use natural language to control the fitting room experience. Customers can ask questions (e.g. “What sizes are available in this color?”) or request actions (e.g. “Call an associate” or “Show me this item in another color”) simply by speaking. This hands-free interaction is particularly useful when the shopper’s hands are full or they are indecisive. It also adds convenience and inclusivity (e.g. for visually impaired users). Voice control can streamline tasks like summoning help or finding information, making the fitting room experience more seamless. As voice recognition technology improves, such assistants can handle complex queries about fit, fabric care, or styling advice without manual input. This enhances customer service efficiency by letting shoppers immediately voice their needs.
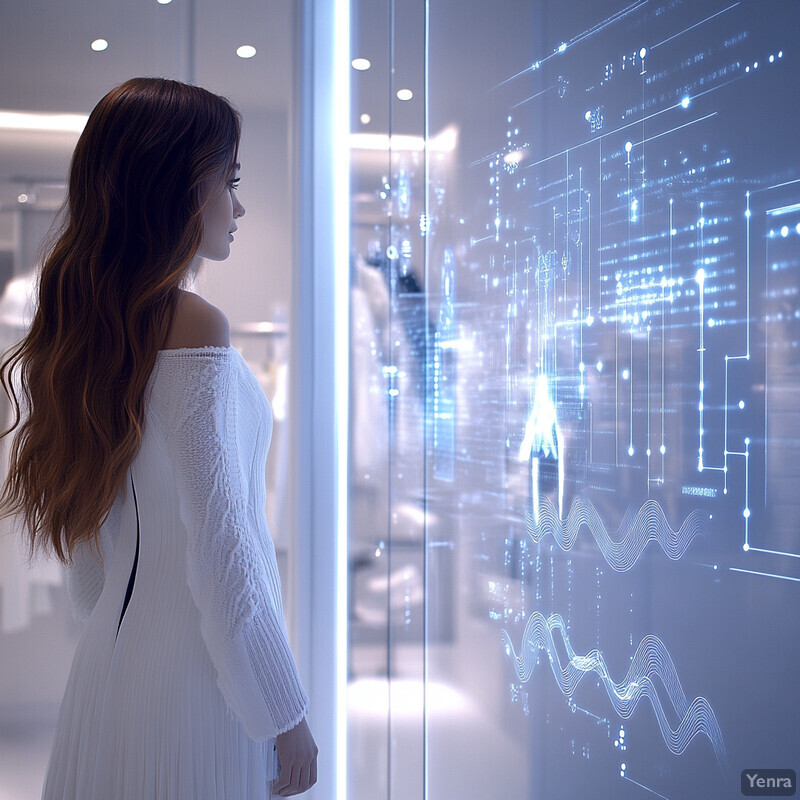

The growing market data underline consumers’ readiness for voice shopping. Bazaarvoice reports that U.S. voice-commerce transactions reached $19.4 billion in 2023 (up from $4.6B in 2021), showing rapid adoption of voice assistants in retail. Virtual assistant usage is widespread: roughly 55–59% of consumers say they want to use bots or AI tools while shopping, and over 80% of shoppers would use AI to help get product information or service. In clothing retail specifically, major brands are already deploying voice interfaces in stores and apps (for example, Alexa in dressing rooms). These trends indicate that shoppers increasingly expect voice options. By adding voice control to fitting rooms, retailers tap into a multi-billion-dollar channel and meet consumer preferences for hands-free interaction and information access.
6. Gesture and Facial Recognition Controls
Gesture and facial recognition let customers interact with the fitting room interface without touch. Users can wave a hand, nod, or make simple movements to navigate menus on smart mirrors or kiosks. Cameras or sensors track these gestures to change outfits, adjust settings, or request assistance. Facial recognition can personalize content by identifying the shopper (e.g. greeting them by name) or inferring mood. These touchless controls improve hygiene (no need to touch screens) and add a futuristic, engaging element. They also simplify access for mobility-impaired users. By eliminating physical contact, gesture controls create a safer, cleaner experience while keeping customers immersed in the tech.
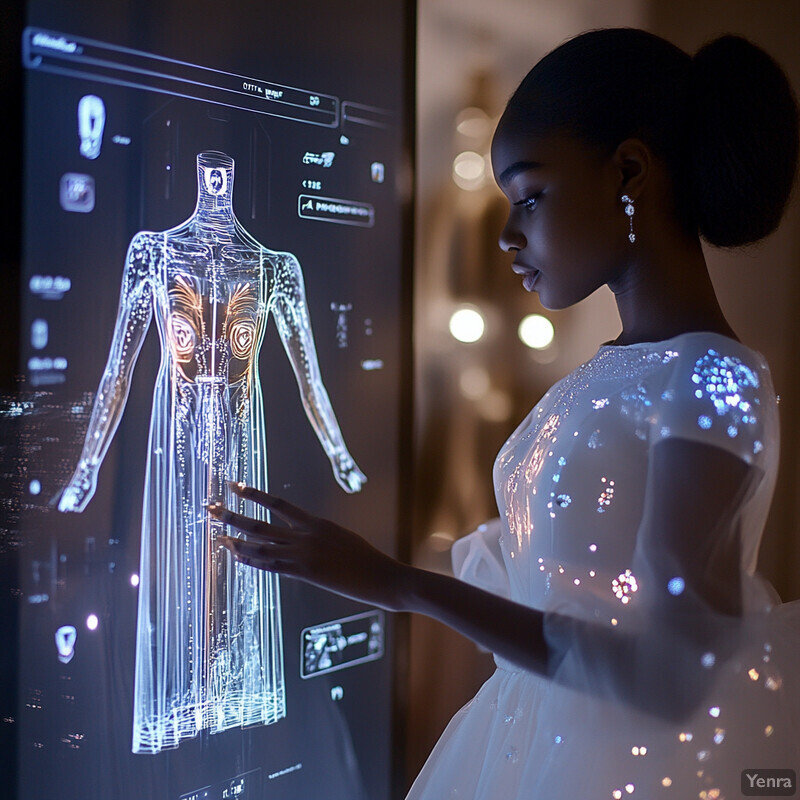

The market for touchless vision-based tech is growing rapidly, driven in part by retail applications. For example, Precedence Research reports that the global gesture recognition market was valued at about $28.96 billion in 2024 and is projected to exceed $165 billion by 2034. Likewise, facial recognition technology (often used for customer identification or sentiment) is a multi-billion-dollar market. While specific academic studies on fitting-room gesture controls are scarce, industry trends confirm widespread adoption: retailers use camera-based systems for both security and interactive displays. This broad market growth indicates that retail environments are increasingly equipped with the sensors and algorithms needed for gesture/face control. However, detailed data on in-fitting-room usage is limited, and design must balance convenience with privacy considerations.
7. Dynamic Lighting and Color Adjustments
Smart fitting rooms can automatically adjust lighting conditions to simulate different environments. For example, the system might brighten lights to mimic outdoor sunlight or warm lights for evening ambience. This lets customers see how the clothing’s colors and textures appear under various conditions. By changing color temperature and intensity, the room ensures that garment shades look true in different scenarios. Such adaptive lighting helps customers judge whether an outfit suits them under daylight, office lights, or nightclub mood lighting. It also enhances the presentation of fabrics, making details more visible. Overall, intelligent lighting customization makes the try-on more informative and can even influence mood and shopping behavior.

Advances in lighting technology support this innovation. According to industry analyses, AI-powered smart lighting systems can “change light levels, colors, [and] patterns in real time” to improve the user experience. For instance, TechnoLynx describes AI-driven lights that learn customer preferences and instantly adjust the fitting room’s hue and brightness. Strong retail lighting has been linked to sales effects: studies indicate well-lit stores encourage shoppers to buy. (One retailer found that customers were over 12% more likely to make a purchase in a brightly lit store than a dimly lit one.) By applying similar principles in fitting rooms, smart lights can highlight garment features, encourage positive shopping psychology, and reduce returns caused by inaccurate color perception. These industry findings suggest that dynamic lighting adds both aesthetic and practical value to the fitting experience.
8. Predictive Stock Management
Smart fitting rooms can integrate with inventory systems to forecast demand. By analyzing what customers try on (and purchase) in real time, the system can alert staff to low stock of popular sizes or styles. AI algorithms predict which items and sizes are needed next, so stores can restock proactively. This ensures that customers are less likely to encounter “size not available” messages in the fitting room. For example, if many shoppers try on size M of a shirt, the system flags that inventory is running low. Employees can then retrieve more stock immediately. This reduces missed sales opportunities due to stockouts. By keeping shelves optimally filled, predictive management also cuts excess inventory, saving costs and waste.

AI-driven demand forecasting is well-known to improve supply chain metrics. Industry sources report that machine learning demand-planning tools can cut inventory costs by around 22% and reduce stockouts by about 18%. In practice, major retailers see significant gains: Walmart, for instance, has leveraged advanced forecasting (now even using GPT-4 models) to automate inventory allocation, resulting in roughly a 30% reduction in stockouts. Analysts also note that companies using AI for supply chain saw up to 25% lower operating costs and 30% higher customer satisfaction. These figures demonstrate that using AI to anticipate demand can keep fitting-room stock aligned with customer interest. In sum, both research and case studies confirm that predictive inventory controls greatly reduce the empty-shelf scenario in fitting rooms.
9. Material and Fabric Insights
AI tools can analyze and report on fabric properties in the fitting room. For instance, sensors might assess a garment’s texture or weave, while software can identify the fabric type (cotton, wool, synthetic) and its characteristics (stretch, durability). The system could then advise on how a fabric will behave (e.g. “this linen will soften after wash” or “this blend resists wrinkling”). Customers would receive instant fabric care tips and realistic previews of how the material drapes on their body. This insight helps shoppers understand garment performance and quality without manual labels. It also enables informed choices for comfort and longevity. By translating technical fabric data into plain advice, AI gives customers confidence in the material aspect of their fit.

Researchers report growing success in AI-driven textile analysis. A 2024 review notes that AI models can now predict fabric properties such as strength, elasticity, breathability, and handfeel with high accuracy. These advances mean systems could flag a garment as “highly stretchable” or “very soft” based on its material composition. For example, machine learning algorithms have been trained to estimate the tensile strength of yarns and the thermal comfort of blends. In retail, this implies a fitting-room app could instantly identify fabric type via image or tag data, then consult AI models to anticipate its behavior (e.g. shrinkage or moisture wicking). Although still emerging in consumer settings, such AI fabric analysis is backed by recent peer-reviewed findings, indicating that material-level recommendations can be automated in near real time.
10. Personalized Cross-Selling and Upselling
In-room AI can suggest complementary or higher-end items to customers. For example, if a shopper tries on a dress, the system might recommend matching shoes, a coordinating scarf, or an upscale version of the dress. It analyzes the customer’s chosen items and past preferences to propose these extras. This seamless upselling and cross-selling feels helpful rather than pushy, since suggestions align with the shopper’s style. It enhances the shopping experience by discovering relevant add-ons. Customers often appreciate these curated suggestions when they truly fit their taste. The result for retailers is increased basket size: customers who get thoughtful accessory recommendations tend to spend more.

Research on AI in retail shows significant revenue gains from personalized selling. A 2024 industry survey found businesses with AI-driven upselling saw about a 15% increase in revenue on average (with e-commerce boosted by roughly 15% and brick-and-mortar by 12%). Furthermore, personalized recommendations drive customer loyalty: about 80% of shoppers say they are more likely to return to a retailer that provides personalized offers and suggestions. This aligns with concrete examples: one retailer using AI stylists reported that tailored recommendations increased its average transaction value. Such data indicate that enabling the smart fitting room to cross-sell related items (based on AI analysis of the customer’s current try-ons) can meaningfully raise sales and repeat visits.
11. Automated Assistant Summoning
Fitting rooms often have “call button” features for on-demand help. With AI, this can be automated and intelligent. A customer can simply say “I need help” or push a touchscreen icon to alert staff. The system can even identify which fitting room triggered the request. Voice assistants or kiosk screens can notify store personnel with the requestor’s preference (e.g. preferred language or assistance type). This streamlines service: customers no longer have to exit to find an employee or awkwardly wave through curtains. It also ensures no customer is stranded for long. By promptly routing assistance requests, automated summoning leads to faster help and better customer satisfaction.

Consumer research highlights the importance of easily accessing assistance in fitting areas. A 2023 survey found that 84% of shoppers report difficulty getting help in a dressing room. To address this, many smart fitting-room systems include a one-touch “call” option on the in-room screen or via voice command. For instance, Aila Technologies notes that its fitting room interface lets customers request a sales associate with a simple tap. In practice, stores using these systems have reported higher purchase rates: one study found 62% of consumers ended up buying more items when they could easily get in-room help. These findings show that automating assistance alerts with AI interfaces is a practical way to solve a common customer pain point and boost conversions.
12. In-Room Digital Concierge
An AI concierge in the fitting room acts like a virtual sales assistant. It can interact via chat or voice to answer questions, display product details, offer styling advice, and locate items in-store. For example, a user might ask “What fabric is this?” or “Show me accessories that match this outfit.” The digital concierge can pull up videos, lookbooks, or brand stories on the fitting-room display. It essentially provides instant customer service information on-demand. This enriches the experience by giving detailed product knowledge or cross-sell suggestions without waiting for a staff member. Shoppers get personalized attention through technology, making them feel guided and reducing friction.

Surveys indicate strong consumer interest in AI helpers during shopping. IBM reports that 55% of consumers want to use bots or virtual assistants while shopping, and roughly 86% of those not yet using AI in-store say they would welcome it for product research. Specifically, about 82% of shoppers say AI could help them “research products or get product information”. In practice, brands are responding: high-end retailers and services (like Macy’s and Neiman Marcus) are testing in-room screens and chatbots for product info. These trends suggest that integrating an interactive digital concierge aligns with customer expectations. When implemented well, it satisfies the demand for convenient, instant information, as reflected by the majority of consumers who want AI-supported shopping tools.
13. Body Composition and Posture Analysis
Beyond basic measurements, AI can assess body composition and posture in the fitting room. Cameras or sensors may estimate attributes like body fat distribution or how a person stands (slouching vs. upright). The system then tailors fit advice to these factors – for example, suggesting styles that complement a particular posture or body shape. It might flag if a garment hangs differently on a postured body, recommending adjustments or alternative cuts. This advanced analysis helps customers find flattering fits for their actual stance and build. Over time, it could even track changes (e.g. fitness progress) and adjust size recommendations accordingly. The result is a hyper-personalized fitting experience that considers the customer’s unique body profile, not just size numbers.
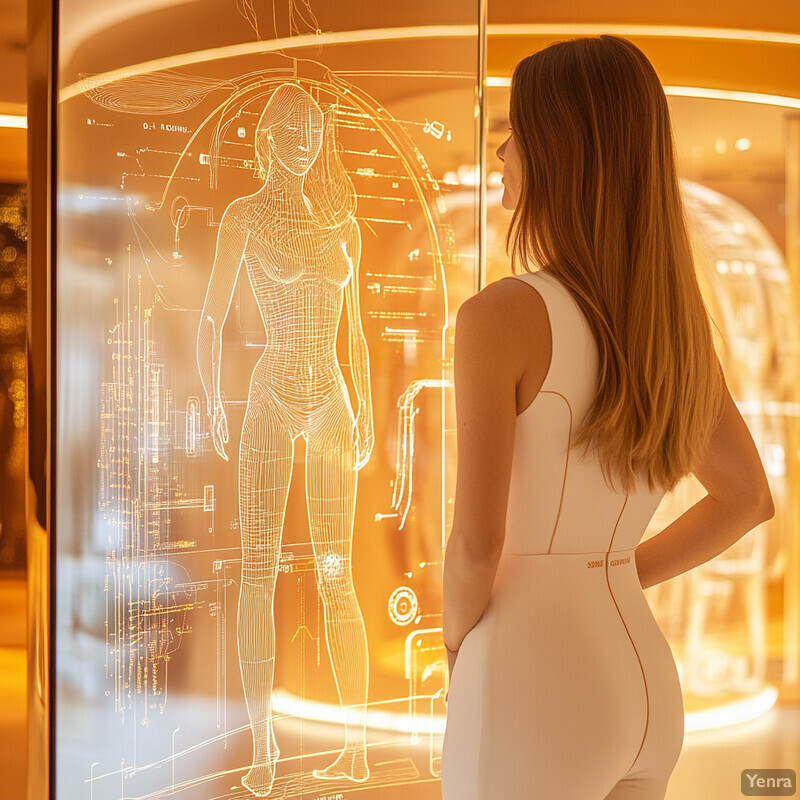
Cutting-edge research is bringing such capabilities closer to reality. For instance, a 2025 report from Cornell University describes “SeamFit” – smart clothing that embeds sensors into fabric to detect a person’s posture and movements. This technology can automatically recognize how the wearer is standing or moving without bulky devices. In the retail context, similar AI techniques could analyze a fitting-room video feed to infer posture. While specific studies on commercial posture recommendations are still emerging, these research prototypes show it is feasible to track and interpret body position. Applying these methods, an AI system could then recommend clothing fits optimized for that posture (for example, advising different cuts for rounded vs. straight shoulders). The underlying AI for posture and composition is validated by such scholarly demonstrations, indicating this feature is plausible for future smart fitting rooms.
14. Cross-Channel Integration
Cross-channel integration means the fitting room syncs with online and mobile channels. For example, if a customer signs in, the fitting room can pull their online purchase history and preferences, and save fitting room data back to their profile. Items tried on in-store can be added to a shared digital cart. The system could also notify the store of an online order awaiting pickup or suggest items based on online browsing. This creates a seamless journey: a garment favorited on the retailer’s app might prompt a fitting room to set aside that item. It also allows loyal customers to access promotions or loyalty points in the fitting room. By unifying physical and digital touchpoints, cross-channel AI ensures a coherent, personalized experience regardless of where the shopping starts or ends.

Omnichannel shoppers heavily use multiple channels in one journey. Industry data show 58% of consumers research products online and then purchase them in-store, and 71% expect to see consistent inventory availability across online and physical stores. Retailers with strong omnichannel systems see higher customer retention: businesses that implement comprehensive channel-integration strategies retain about 89% of their customers versus 33% for those that don’t. Moreover, omnichannel customers spend roughly 30% more than single-channel shoppers. These figures underscore the importance of integrating the fitting room into the overall retail ecosystem. They suggest that enabling the fitting room to “talk” with mobile apps and online accounts – updating profiles and inventories in real time – can increase sales and loyalty by meeting consumer expectations for a connected experience.
15. Preference Learning Over Time
Over multiple visits, smart fitting rooms can learn a shopper’s evolving style preferences. Each try-on provides feedback (e.g. which sizes fit, which styles they keep or return). The AI aggregates this data to refine its suggestions on future visits. For example, if a customer consistently prefers slim-fit cuts or certain color palettes, the system notes this and prioritizes those. It might also remember size changes over time (e.g. seasonal weight fluctuations) and adjust fit advice accordingly. By continuously learning from each interaction, the fitting room becomes more personalized for returning customers. Ultimately, this creates a more fluid, tailored experience where the system “gets to know” the shopper’s tastes and automatically improves recommendations.

Longitudinal personalization is proven to drive results. For instance, Aila’s research shows that customers are 62% more likely to purchase additional items when their experience is personalized. In another study, “complete-the-look” style recommendations increased conversion and cross-sell rates by 30–40%, benefits that accrue when the system has learned what combinations appeal to shoppers. Furthermore, retailers using AI to adapt to user feedback often see sustained lift in customer lifetime value. Although academic studies on fitting-room systems are limited, these industry findings indicate that continuously refining recommendations based on user behavior (ratings, purchases, returns) yields measurable gains. In short, integrating feedback loops (e.g. customer ratings or success of recommendations) enables the AI to improve over time, matching the efficiency of personalized services seen on other platforms.
16. Automated Privacy Controls
Privacy controls in smart fitting rooms help customers feel secure. For example, cameras can be deactivated or pixelated when no one is in the room, ensuring no accidental recording. The system can alert users before scanning or recording begins, and only store data needed for the fitting experience. Digital signage may remind customers that only non-identifying measurements (not images) are saved. Some systems blur faces or delete data immediately after use. By design, sensors may only activate when the user explicitly requests a service (like virtual try-on), otherwise preserving privacy. These measures build trust by preventing unauthorized data capture. Transparent privacy settings – e.g. easy opt-out buttons – allow shoppers to control what information is collected.

Privacy concerns are a major consumer consideration in technology use. Academic research confirms that even advanced fitting technologies raise worries: one study notes that many users remain anxious about sharing detailed body measurements with retailers. In fact, the concept of a “privacy paradox” appears in studies: while customers see the benefits of 3D scanning, they also express significant concern about personal body data collection. This underscores the importance of robust privacy measures in deployment. In retail practice, regulations often prohibit cameras in dressing rooms, so many systems use “privacy mode” by default. For instance, Bodystickers and other devices employ image obfuscation until the customer consents. Although specific data on smart fitting rooms’ privacy controls are limited, experts stress that measures like data encryption, automatic data deletion, and clear consent protocols are essential to address consumer wariness.
17. Eco-Friendly Recommendations
Eco-friendly AI suggests sustainable alternatives in the fitting room. When a customer tries on an item, the system can highlight versions made from organic, recycled, or low-impact materials. It might display the carbon footprint or water use of the chosen garment and compare it to greener options. Additionally, the system could recommend eco-friendly care instructions (e.g. cold wash, line dry) or even rental/resale options if a new purchase isn’t essential. This conscious filtering helps shoppers align purchases with environmental values. By guiding consumers toward sustainable fashion choices, the fitting room technology promotes responsible consumption. It also educates shoppers on the impact of materials and encourages more thoughtful buying decisions.

Sustainability has become a key factor for many shoppers. Surveys show that approximately 85% of consumers have been personally affected by climate change and prioritize sustainability. Notably, PwC found that consumers are willing to pay about 9.7% more for sustainably produced goods. In apparel, brands like Zara committing to 100% sustainable fabrics by 2025 reflect this demand. While no peer-reviewed study specifically measures in-room eco-recommendations, industry analysis makes clear that offering eco-friendly options can boost customer goodwill and sales. For example, retailers that highlight sustainable items often see higher loyalty and justify small price premiums. The combination of consumer surveys and retailer commitments indicates that an AI recommending greener choices would meet a real desire: customers favor brands that facilitate sustainable purchasing, and are even willing to spend more on such products.
18. Multilingual and Cultural Adaptability
Multilingual support lets shoppers interact in their preferred language or cultural context. The system can offer voice and text interfaces in multiple languages (e.g. Spanish, Mandarin, French), so non-English speakers or tourists can easily navigate fitting-room features. It can also adapt visuals and recommendations based on cultural norms (such as modesty preferences or color meanings). For example, the AI could automatically switch to a language matching the shopper’s profile, or recognize cultural size conventions. This inclusivity ensures foreign or minority customers receive the same level of personalized service. Supporting multiple languages and culturally relevant options makes the fitting experience accessible and comfortable for a wider audience, increasing global appeal.

As retail goes global, localization is crucial. Experts note that providing content in multiple languages greatly expands a product’s market reach. One analysis found that over 70% of consumers prefer shopping in their native language, leading to higher engagement (especially in non-English markets). By enabling multiple language options in-store, retailers can capture sales from international tourists and multilingual local communities. For instance, Visa’s digital shopping index highlights that U.S. consumers regularly use a range of digital tools, implying that language flexibility enhances adoption. In practice, brands that localize their apps and in-store tech report improved customer satisfaction and higher retention. In summary, experts emphasize that global retail success requires AI systems to handle diverse languages and cultural nuances, making fitting-room tech more universally user-friendly.
19. Emotional Sentiment Analysis
Emotion recognition enables the system to respond to shoppers’ feelings. Cameras or microphones analyze facial expressions, tone of voice, or gestures to gauge mood (happy, frustrated, confused, etc.). For example, if the AI detects the shopper looks frustrated, it might proactively simplify options or offer assistance. If the customer smiles, it might highlight similar styles. The fitting room could even adjust music or lighting to match the detected mood. By adapting in real time to customer sentiment, the store creates a more empathetic experience. This emotional tuning can make shopping feel more personalized and sensitive, helping staff know when to engage or step back.

The emotion recognition market is rapidly expanding across retail applications. A recent industry report values the global emotion detection and recognition market at $37.8 billion in 2024, with projections to grow to over $113 billion by 2032. Companies like Microsoft and Google offer APIs that detect facial cues and sentiment, and retailers are exploring these tools to measure customer reactions. Research shows that using sentiment analysis can improve marketing and customer service by identifying satisfaction or frustration signals. While academic studies on fitting-room mood analysis are just emerging, the sizable market investment indicates retailers believe emotion AI can enhance engagement. In practice, pilot projects (e.g., MoodMe’s emotion-detecting mirrors) report higher user engagement and valuable analytics. This evidence suggests that sentiment analysis can dynamically personalize the shopping environment, with the emotion-detection industry’s strong growth reflecting its perceived retail value.
20. Continuous Learning from Feedback
In a continuously learning system, the fitting room refines its recommendations using direct customer feedback. When shoppers rate suggestions, leave comments, or choose to try on and purchase certain items, the AI updates its model. For example, if a user dismisses a recommended shirt style, the system learns to avoid similar suggestions for that person. If another customer reorders past favorites, the AI strengthens those patterns. This ongoing feedback loop ensures the recommendations stay up to date with the customer’s current tastes and any changes in fit. Over time, the system becomes finely tuned to each user’s evolving preferences and sizing nuances. The result is a progressively better personalized experience: as the AI learns, it provides increasingly relevant fit and style advice.

The power of iterative learning is supported by retail evidence. For instance, personalization strategies that adapt to user behavior can boost key metrics significantly. BCG reports that providing “complete-the-look” suggestions can increase conversion and cross-sell by up to 30–40%, gains that compound as the system refines its understanding. Likewise, empirical data show that shoppers presented with tailored options tend to spend more – one study found 62% of consumers buy more items when served a personalized experience. These improvements hinge on the AI’s ability to update itself with feedback (purchases, clicks, returns). While these studies are broader than fitting rooms specifically, they demonstrate that continuous learning from each customer interaction drives higher satisfaction and sales. In summary, implementing feedback-driven learning in a smart fitting room aligns with proven personalization gains – the more data it gathers, the smarter and more effective its recommendations become.