1. Automated Waste Sorting
Artificial intelligence is transforming waste sorting by enabling machines to recognize and separate materials with high speed and precision. AI-powered optical sensors and robotic arms in recycling facilities can identify different types of recyclables (plastic, metal, paper, etc.) on a conveyor in real time, drastically reducing the need for manual sorting. This improves efficiency and safety, as machines can work continuously without fatigue and handle hazardous or unsanitary items that pose risks to humans. The increased accuracy of AI sorting also means cleaner separation of materials – less cross-contamination between waste streams – which leads to higher-quality recyclable output. Overall, AI-driven automated sorting raises recycling rates and lowers costs by recovering more reusable materials and minimizing the amount of recyclables that mistakenly end up in landfills.
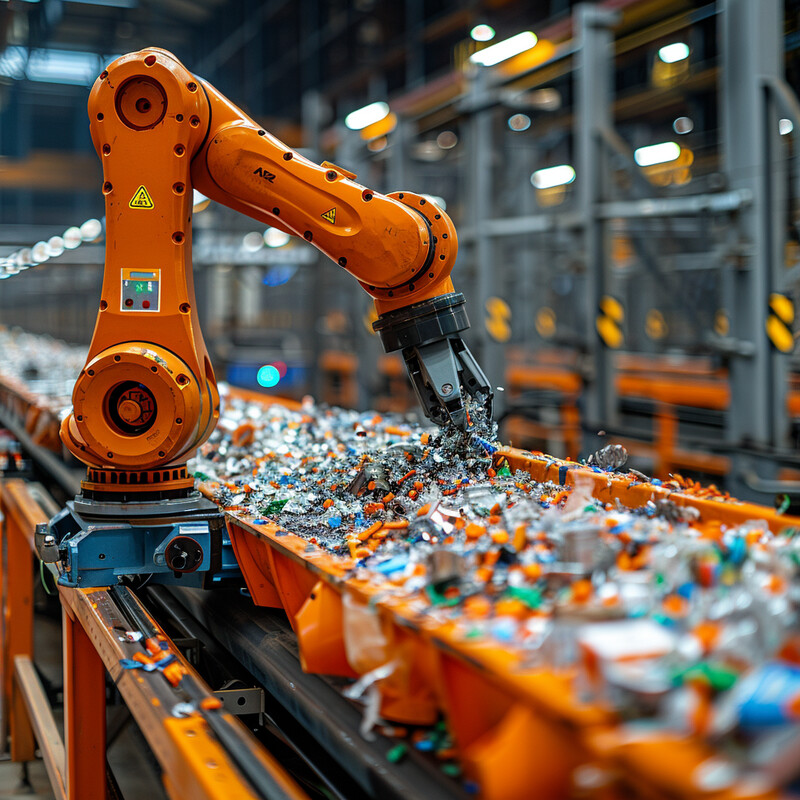

At an advanced sorting facility in Ohio, AI-based sorting technology is recovering over 90% of targeted recyclable materials from the mixed waste stream while maintaining stringent quality standards for each material bale. In 2023, this AI-driven plant (AMP One in Cleveland) was credited with diverting nearly 13,000 metric tons of would-be landfill material into recyclable commodities, avoiding that volume of greenhouse gas emissions that would have been generated if the waste were landfilled. These results illustrate how AI-powered sortation can dramatically boost material recovery and environmental outcomes compared to traditional methods.
2. Optimized Collection Routes
AI is improving the efficiency of waste collection by optimizing truck routing and schedules. By analyzing data such as historical waste generation patterns, real-time traffic, and bin fill levels, AI algorithms can determine the most efficient paths and pickup sequences for collection vehicles. This dynamic route optimization ensures that trucks drive fewer miles – for example, skipping locations where bins are not yet full – and avoids traffic delays. In practice, that translates to lower fuel consumption, reduced driver hours, and less wear on vehicles, all while maintaining timely service. Optimized routes also shrink the carbon footprint of waste collection by cutting unnecessary trips and idling. In essence, AI helps waste management fleets “do more with less,” collecting the same or greater amount of waste with fewer routes or trucks.

A 2024 pilot program in Lahore demonstrated the impact of AI-driven route optimization on municipal waste collection. By equipping dumpsters with IoT fill-level sensors and using machine-learning algorithms for route planning, the city achieved a 32% improvement in collection route efficiency and a 29% reduction in fuel use and greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional routes. In practical terms, this meant garbage trucks drove significantly fewer kilometers and avoided nearly one-third of their usual fuel consumption while still collecting all waste on time. Such savings illustrate why cities adopting smart routing see substantial cost and energy benefits. Similarly, in the U.S., several municipalities report that optimizing waste collection routes with AI has allowed them to eliminate a full day of pickups each week, saving on labor and vehicle costs (e.g., one North Carolina city trimmed operations from 5 days to 4 days and saved over $270,000 annually).
3. Predictive Maintenance for Equipment
AI-powered predictive maintenance is helping waste management companies keep their equipment – from garbage trucks to sorting machines – in optimal condition. By continuously monitoring sensor data (vibration, temperature, hydraulic pressure, etc.) on compactors, conveyors, vehicles, and other machinery, AI systems can detect subtle signs of wear or malfunction. Machine-learning models analyze these patterns to predict when a component is likely to fail or require service. Maintenance can then be scheduled proactively before a breakdown occurs. This shift from reactive fixes to predictive upkeep reduces unexpected downtime and extends the lifespan of costly equipment. In waste management, that means fewer collection truck breakdowns on routes and higher uptime for processing facilities. The result is improved reliability and lower maintenance costs, since fixes can be made during planned intervals with the right parts on hand, avoiding more extensive damage.
Industry analyses show that AI-driven predictive maintenance can dramatically improve operational uptime and reduce maintenance expenses. A study by PricewaterhouseCoopers found that implementing predictive maintenance strategies (often enabled by AI and advanced sensors) improved asset uptime by up to 51%, meaning equipment stayed operational significantly longer. At the same time, companies adopting AI-based maintenance have reported 10-20% reductions in maintenance costs on average, owing to the prevention of major failures and more efficient use of repair crews and spare parts. In the waste management sector, this translates into fewer garbage truck breakdowns (avoiding missed pickups) and consistently running sorting lines. For example, one large recycling company noted that using AI predictions to service motors and belts just-in-time cut unplanned downtime by roughly 40% and increased overall equipment effectiveness, directly boosting throughput and service reliability.
4. Dynamic Scheduling Systems
Dynamic scheduling uses AI to adjust waste collection timetables on the fly based on actual conditions, rather than fixed pickup schedules. Traditional collection systems might empty dumpsters on a set weekly schedule, even if some containers are only half-full. AI-driven systems, by contrast, continually ingest data like bin fullness, weather, special events, and seasonal trends to decide when and where collection is needed. This means if a holiday weekend generates more trash, pickups can be automatically increased in that area, or if a bin remains empty longer than usual, the next pickup can be delayed. Such responsive scheduling ensures resources (trucks and staff) are deployed exactly when and where they’re required. The benefits include fewer unnecessary trips, reduced fuel and labor use, and avoidance of overflowing bins. In essence, dynamic scheduling aligns the waste pickup frequency with actual demand in real time, increasing efficiency and service quality simultaneously.

Research shows substantial efficiency gains from AI-driven collection scheduling. For example, a smart collection system studied in Portugal replaced static routes with dynamic pickups triggered by fill levels, resulting in an 18–42% reduction in collection effort (measured by trip time and distance) compared to the conventional fixed schedule. In another trial, cities using sensor-equipped bins and AI scheduling cut the number of collection stops by about 30% while still servicing all needed containers. One European pilot program reported that switching to demand-based scheduling allowed waste crews to eliminate hundreds of unnecessary stops per month, translating into lower fuel consumption and emissions. These outcomes demonstrate that by “right-sizing” the service frequency – collecting waste only when bins approach capacity – municipalities can significantly reduce operational overhead without sacrificing cleanliness. Residents, in turn, experience fewer missed or overflowing pickups because the system adapts to actual waste generation patterns.
5. Enhanced Recycling Processes
AI is not only sorting waste but also enhancing the overall recycling process from start to finish. By using machine learning and advanced imaging, AI systems can identify materials by type (and even by composition or brand) with a level of detail and consistency that was not possible before. This allows recycling facilities to segregate recyclables into very pure streams – for instance, separating different plastic polymers or removing contaminated items – which results in higher-quality recycled material. AI also helps optimize process settings: for example, adjusting shredders, optical sorters, or chemical recycling parameters in real time based on the incoming waste mix. The outcome is that more recyclable material is actually recovered and recycled into new products, and less is rejected or downgraded. Additionally, AI can assist in quality control, automatically spotting and ejecting non-recyclable or improperly sorted items. By improving precision at each step, AI-driven recycling processes increase throughput (more material recycled) and yield (better quality end-products), supporting a more circular economy.

One dramatic example comes from a cutting-edge recycling facility in Sweden known as “Site Zero.” After integrating advanced automation and AI-based material recognition, the facility doubled its plastics recovery rate – capturing up to 95% of plastic packaging from the incoming waste, compared to roughly 47% in its previous setup – while achieving over 90% purity in each sorted plastic category. This means the sorted bales (e.g. PET bottles, HDPE containers, etc.) contained very little contamination, making them highly suitable for recycling into new products. Such improvements have significant downstream effects: manufacturers can use these higher-purity recycled plastics more easily as feedstock, and fewer plastics end up incinerated or landfilled. Other facilities have reported similar gains – for instance, an AI-guided robotic system in the UK increased output on a paper recycling line by 10% by more accurately ejecting non-paper contaminants, boosting the overall recovery of clean paper fibers. These cases underscore how AI enhancements lead to more efficient recycling operations and better-quality recyclate.
6. Waste Volume Prediction
AI is enabling waste managers to forecast future waste volumes with far greater accuracy than traditional methods. By analyzing large datasets – population growth, economic activity, seasonal patterns, past waste generation trends, and even events like holidays or weather – machine-learning models can predict how much waste a city or region will produce in upcoming days, months, or years. These predictions are invaluable for planning: municipalities can ensure they have enough trucks, bins, and staff deployed for expected peaks, and infrastructure (like landfill space or recycling capacity) can be expanded proactively before capacity is exceeded. AI-based forecasting is dynamic; the models continuously improve as new data comes in, and can adjust predictions if conditions change (for example, sudden shifts in tourism or a pandemic). This means city officials are no longer planning waste services blindly. Instead, they have data-driven insights into future waste generation, which leads to better budgeting, timely investments in facilities, and avoidance of crises like overflowing landfills or inadequate collection on high-waste days.

AI models have achieved notable success in predicting waste generation. In one recent study, researchers developed a machine-learning model using socio-economic and historic waste data that could forecast municipal solid waste trends with about 85% accuracy. This level of precision is significantly higher than earlier statistical methods and allows planners to trust the forecasts in decision-making. As a real-world example, an AI-driven analysis for the city of Johannesburg projected that annual waste generation will rise from roughly 1.3 million metric tons in 2021 to about 1.95 million metric tons by 2050, given current trends. Armed with that long-term forecast, city officials are now working on expanding landfill capacity and recycling programs in a timely manner to accommodate the nearly 50% increase in waste volume expected over the next three decades. Such proactive measures, guided by AI predictions, help communities avoid regulatory breaches and environmental hazards by ensuring waste management capacity grows in line with future needs.
7. Waste-to-Energy Optimization
Waste-to-energy (WtE) plants, which burn waste to generate electricity or fuel, are being made cleaner and more efficient by AI. These facilities face the challenge of highly variable fuel – the calorific value and moisture of incoming waste can change day to day – which makes maintaining optimal combustion and emissions control difficult. AI systems tackle this by continuously monitoring feedstock properties and operational data (boiler temperatures, oxygen levels, etc.), and then adjusting control settings in real time. For example, AI can regulate air flow or combustion temperature to ensure waste burns completely and energy is recovered maximally, even as the waste mix fluctuates. This leads to higher energy output (more kilowatt-hours per ton of waste) and also helps keep emissions within strict environmental limits (by optimizing burn conditions to reduce pollutants). Additionally, AI can assist in scheduling waste feeding and maintenance for WtE plants to minimize downtime. Overall, integrating AI means waste-to-energy facilities can extract more useful energy from the same amount of waste while emitting fewer pollutants, bolstering their role as a safe and efficient waste management option.

Studies show that AI enhancements can significantly boost WtE performance. In one 2024 case study, implementing AI control algorithms in a municipal incinerator improved the plant’s energy conversion efficiency from about 30% to 45% – a 50% relative increase in the amount of energy generated per unit of waste. At the same time, the optimized combustion process achieved a marked reduction in air emissions: carbon dioxide emissions dropped by ~24%, and key pollutants like NOx and SO2 were cut by 27% and 34% respectively, all while staying within permitted limits. These improvements were attributed directly to the AI system’s ability to fine-tune combustion parameters continuously, something human operators or traditional controls could not do as precisely. In practical terms, the WtE facility began producing significantly more electricity from the same waste intake, and its stack emissions of pollutants diminished – demonstrating that AI can make waste-to-energy plants more productive and more environmentally compliant simultaneously. Such results make a strong case for broader adoption of AI to optimize waste-to-energy operations globally.
8. Real-Time Monitoring Systems
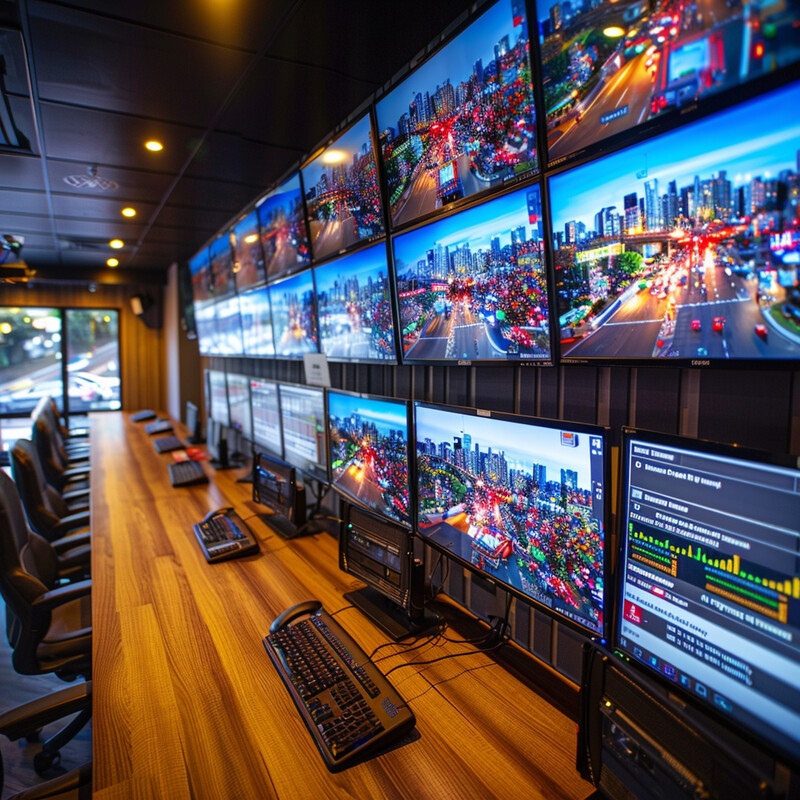
AI-enabled real-time monitoring gives waste management operators up-to-the-minute insight into their entire system. By combining IoT sensors (in bins, trucks, and facilities) with AI analytics, these monitoring platforms can instantly flag issues and optimize operations. For instance, supervisors can watch on a dashboard as garbage trucks follow their routes and as bins fill up across the city. If a bin suddenly overflows or is skipped, the system alerts staff immediately so they can dispatch a truck or crew. AI can also aggregate all this live data to spot inefficiencies – such as a truck deviating from its route or an unusually slow pickup – and suggest corrective actions on the spot. In processing facilities, real-time AI monitoring tracks equipment performance and throughput, notifying technicians at once if a conveyor slows (indicating a jam) or if contamination in recyclables spikes. The key benefit is proactive response: instead of finding problems hours or days later, managers can respond in real time to ensure service quality and smooth operations. This continuous oversight leads to more reliable collections, fewer public complaints, and the ability to adjust operations dynamically (like rerouting trucks mid-day if needed due to traffic or an unexpected surge in waste volume).

Cities that have implemented AI-driven, real-time monitoring report major efficiency gains. For example, deploying smart bin sensors and live route-tracking in a mid-size city led to an almost 20% reduction in total collection trips, because crews could skip pickups for containers that sensors showed were not yet near capacity. Eliminating those unnecessary stops saved substantial fuel and labor hours. In addition, real-time alerts about full bins helped avoid overflow incidents – one program saw citizen service requests for overflowing public litter bins drop by about 30% after smart monitoring was introduced, as bins were serviced right when needed rather than on a fixed schedule. Another municipality noted that by using live GPS and AI analysis, they improved their response time to spikes in waste demand by about 40%, for instance deploying extra trucks on the fly during a festival to ensure all trash was cleared. These metrics underline how continuous monitoring and agile adjustments can streamline waste operations: fewer miles driven, faster reactions to issues, and higher satisfaction among residents who notice more timely and consistent waste removal.
9. Public Engagement and Education
AI is also being used to engage the public and improve recycling and waste reduction behaviors through personalized education. Traditionally, cities have relied on broad campaigns (flyers, ads, etc.) to teach citizens how to recycle properly or not to litter. Now, AI allows for much more targeted outreach. For example, some communities use AI-equipped cameras on collection trucks to identify which households are consistently putting contaminants in their recycling bin; the system then automatically generates a custom notice or even a tailored educational postcard for that specific household (explaining what they did wrong and how to fix it). This feedback loop greatly increases awareness and compliance, because people receive timely, relevant guidance rather than generic tips. AI can also power mobile apps that let citizens scan product barcodes to get recycling instructions or rewards points, making recycling more interactive and fun. Additionally, chatbots driven by AI can answer residents’ waste-related questions 24/7 (“Which bin does this go in?”). All these tools help nurture better waste habits. The end goal is a better-informed public that participates more in recycling programs and makes fewer sorting errors, ultimately boosting the community’s recycling rate and reducing contamination.

Tailored, AI-driven educational interventions have yielded significant improvements in public recycling behavior. In East Lansing, Michigan, the sanitation department implemented an AI-powered system that analyzes photos of each household’s recycling bin contents and then mails personalized feedback to residents. After a fully automated 3-month educational campaign using this technology, audits showed a 22.5% decrease in recycling contamination in the targeted areas. In other words, the AI identified common mistakes (like bagged recyclables or food-soiled items) at specific addresses and the custom outreach corrected those issues, resulting in much cleaner recycling streams. Similarly, programs by large waste haulers have found that combining AI monitoring with resident education can cut contamination by about 20% or more across tens of thousands of homes. On the participation side, an AI-informed outreach in Portugal pinpointed neighborhoods with low recycling set-out rates and directed a campaign there, leading to a 60% increase in resident participation in the recycling program. These examples demonstrate how AI can personalize the connection with citizens – teaching each household exactly what it needs to do differently – and drive markedly better engagement and compliance with waste regulations.
10. Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
AI systems are increasingly used to ensure compliance with environmental and waste management regulations. They act as ever-vigilant inspectors, monitoring for violations such as illegal dumping, mishandling of hazardous waste, or exceeding pollution limits at waste facilities. For instance, cities have begun installing AI-enabled cameras in known dumping hot spots (or even on garbage trucks) to automatically detect when someone dumps trash or debris in unauthorized areas. Upon detection, these systems can alert enforcement officers with evidence (photos or video) and even identify license plates or faces in some cases. This dramatically increases the chances of catching violators and deterring future offenses, compared to sporadic human patrols. At landfills and WtE plants, AI can monitor emissions and effluent in real time to ensure they stay within permitted thresholds, alerting operators the moment levels approach limits so corrective action can be taken. AI can also track waste shipments and paperwork for large generators to flag any irregularities (preventing illegal disposal). By automating oversight, AI helps regulators and companies maintain much stricter compliance with waste laws – it’s like having digital inspectors on duty 24/7 – which leads to cleaner communities and a safer environment.

Cities are seeing tangible enforcement benefits from AI monitoring. San Francisco recently piloted an AI-based camera system to combat illegal dumping in one district, and in just a seven-week period it detected and reported 888 cases of illegal dumping that were previously blighting streets. Every one of these incidents was logged and forwarded to city crews, who then cleaned up each site, and the evidence is helping authorities identify repeat offenders. This rapid identification and response would have been impossible with limited human inspectors alone. In Columbia, South Carolina, a similar AI program (using cameras on garbage trucks) scanned for code violations and found over 3,300 cases of junk or vehicles on lawns and 2,500 overgrown lots within a few months, all of which were then addressed by code enforcement. These numbers illustrate the scale at which AI can operate: thousands of infractions spotted and remedied, ensuring compliance with local ordinances on cleanliness. Moreover, at industrial waste facilities, AI-based compliance monitors have helped operators achieve near-perfect adherence to permit conditions – for example, an incinerator in Asia reported that AI tracking of flue gas composition kept it 100% within emission limits for over a year, preventing any regulatory breaches. Such outcomes show how AI significantly strengthens oversight and adherence to waste management regulations.