1. Energy Management
Artificial intelligence plays a pivotal role in home energy management by optimizing power usage across various devices. Machine learning algorithms learn a household’s energy consumption patterns and make real-time adjustments to thermostats, lighting, and appliances for maximum efficiency. For instance, an AI-equipped smart thermostat can preemptively tweak heating or cooling based on occupancy, time of day, or even weather forecasts, thereby reducing energy waste. These intelligent adjustments not only lower utility bills but also lessen the home's environmental footprint by conserving electricity. In addition, AI can integrate home devices with smart grids or utility pricing signals, scheduling high-energy tasks (like running a dishwasher or charging an EV) during off-peak times when electricity is cheaper and cleaner. Overall, AI-driven energy management systems create more sustainable and cost-effective homes through continuous, adaptive optimizations.
As of late 2022, about 19.6 million smart thermostats had been installed in U.S. homes, a trend that helped cut nationwide heating and cooling energy usage by roughly 1.4% compared to what it would have been without these AI-driven devices (indicating significant energy savings on a large scale).
2. Security Enhancement
AI-driven smart security systems use facial recognition and behavioral pattern detection to distinguish authorized residents from potential intruders. These systems continuously analyze camera feeds and sensor data to recognize familiar faces or expected activities, allowing them to filter out normal household motions from true threats. For example, an AI-enabled security camera can tell if a person at the front door is a family member or an unknown visitor, triggering an alert only when necessary. Beyond intruder detection, AI enhances safety by monitoring for hazards like smoke, fire, or water leaks and instantly notifying homeowners (and even emergency services) of abnormal conditions. Over time, the AI learns the routine of the household – if it detects unusual activity (such as movement in a normally unoccupied area or at an odd hour), it can flag it for review. This intelligent, proactive monitoring reduces false alarms and improves response times, making home security systems more reliable and effective.

Recent industry research shows that about 45% of U.S. internet-connected households now have some form of smart home security solution in place, and approximately 32% of households pay for a professional security service or monitoring subscription to complement these AI-enhanced systems (as of early 2025).
3. Voice Command Improvements
AI has dramatically improved voice command capabilities in smart homes. Modern voice assistants (such as Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri) leverage advanced natural language processing and machine learning to understand user commands and queries with high accuracy. They can interpret different accents and pick up commands even in noisy environments or from across the room, making voice control more reliable in real-life home settings. The AI behind these assistants continuously learns from each interaction, refining its speech recognition and understanding of context over time. As a result, users can effortlessly control lights, thermostats, music, and other devices with simple spoken commands, creating a seamless hands-free experience. These improvements have also expanded language support and enabled more conversational interactions – users can ask follow-up questions or give complex requests, and the AI can handle them in stride. Overall, voice interfaces in smart homes have become more natural and convenient, largely due to AI’s ability to better “hear” and “comprehend” what humans say.

Voice-activated smart technology has become ubiquitous – as of 2023, an estimated 85.4 million Americans use Google Assistant, 81.1 million use Apple’s Siri, and 73.7 million use Amazon’s Alexa for hands-free tasks and home control, reflecting the widespread adoption of AI-based voice interfaces in daily life.
4. Predictive Maintenance
AI-driven predictive maintenance is transforming how homeowners maintain appliances and home systems by anticipating problems before they cause breakdowns. Smart appliances and HVAC systems now often come with built-in AI that monitors performance metrics (like temperature, vibration, or energy draw) continuously. By analyzing this data, the AI can detect subtle signs of wear or irregular operation in devices such as furnaces, air conditioners, or washing machines. This allows the system to alert the homeowner – or a service provider – about a potential issue (for example, a part nearing failure) before it escalates into a complete breakdown. Taking preemptive action (like replacing a component or scheduling a tune-up when prompted) helps avoid unexpected appliance downtime and can extend the lifespan of the equipment. It also means maintenance can be performed at convenient times rather than dealing with emergency repairs. In short, AI turns home maintenance from a reactive chore into a proactive routine, saving homeowners from costly repairs and inconvenience by catching problems early.

Consumers are rapidly adopting AI-enabled appliances that support these predictive maintenance features – in 2023, global spending on smart home appliances was roughly $21.5 billion, and this figure is projected to double in a few years (the worldwide smart kitchen industry alone is forecast to reach about $43 billion by 2027), indicating the growing prevalence of smart devices that can self-diagnose and signal when they need maintenance.
5. Personalized Experience
AI enables a highly personalized smart home experience by tailoring device behaviors and settings to individual preferences. Over time, an AI-powered system learns each household member’s routines and likes – for example, what temperature they prefer at different times of day, what music or lighting they enjoy in the evenings, and their typical daily schedule. Using this knowledge, the smart home can automatically adjust the environment to suit the person. Imagine the lights dimming, window shades closing, and your favorite relaxing playlist starting as you begin your evening reading – all without you saying a word, because the AI anticipates your routine. These systems also adapt: if your schedule changes or you indicate new preferences, the AI updates the automation rules accordingly. The result is a home that “knows” you – it can greet you with personalized settings (lighting, temperature, multimedia, etc.) when you arrive and smoothly transition scenes as you move from waking up, to working, to leisure time. By continuously learning and refining these customizations, AI makes the smart home experience more convenient, comfortable, and uniquely suited to each user.

A 2024 consumer survey found that “improved convenience” is the number-one reason people adopt smart home technology – 46% of respondents cited convenience as their primary motivator for using smart devices (far above other reasons like security or energy savings). This underscores how important personalized, automated experiences are to users, as AI personalization is a key driver of the convenience that smart homes offer.
6. Health Monitoring
AI in smart homes is increasingly being used to monitor and improve residents’ health and wellness. One application is environmental monitoring: AI-equipped air quality sensors can detect issues like high carbon dioxide levels, pollen, or smoke in the air and then automatically activate air purifiers or ventilators to maintain healthy indoor air. Similarly, smart thermostats and humidifiers use AI to adjust home climate settings (temperature, humidity) to optimal levels that promote better sleep and comfort, sometimes even learning what conditions an individual sleeps best in. Another aspect is integration with health data – for instance, a smart home system might take input from wearable devices or smart mattresses that track sleep patterns and vital signs. The AI can analyze this information to identify trends (perhaps noticing that a cooler bedroom leads to deeper sleep) and then adjust the home environment or provide recommendations accordingly. By learning an individual’s health needs and routines, the smart home can do things like dim lights and reduce noise when it senses the person is sleeping, or gently brighten lights in the morning to aid waking up. In essence, AI transforms the home into an active partner in wellness, subtly adjusting the environment to help occupants breathe cleaner air, sleep better, and generally live in healthier conditions.

Consumer use of health-related smart devices is on the rise – an estimated 1 in 3 Americans has tried using a sleep-tracking device (such as a smart watch, fitness band, or bed sensor) to monitor their sleep patterns, and about 78% of those users report that these gadgets have been helpful in improving their sleep habits or overall sleep quality. This trend reflects people’s growing comfort with AI-driven health monitoring in daily life.
7. Enhanced Connectivity
Enhanced connectivity in smart homes refers to AI’s ability to link various devices into a cohesive, interoperable system. Instead of functioning in isolation, smart thermostats, lights, speakers, refrigerators and more can all communicate with each other through a central AI hub or platform. The AI manages this web of connections, translating and routing information between devices (often across different brands or protocols) so that they work in concert. For example, if a smart door lock is opened, the AI can signal the smart lights to turn on and the security camera to deactivate its alarm mode – a coordinated response across devices. AI also optimizes network performance by prioritizing important device communications (ensuring, say, that a fire alarm signal isn’t delayed by less urgent traffic on the network). By learning the household’s usage patterns, the AI might, for instance, anticipate when to start the robotic vacuum after everyone has left and pause it when someone returns. In short, AI acts as the “brain” of the smart home, ensuring that the dozens of connected gadgets – from appliances to sensors – all work together seamlessly and respond intelligently to the occupants’ needs and behaviors. This results in a smoother user experience, where the technology in the home feels integrated and responsive as a whole.

Today’s homes often contain a multitude of smart gadgets – in the United States, the average smart home has around 8 connected smart devices. This highlights the importance of AI-driven coordination, as managing interactions among so many devices manually would be impractical without an intelligent, connective hub ensuring everything works together smoothly.
8. Automated Cooking Appliances
AI-powered cooking appliances bring automation and precision to the kitchen, making it easier to cook perfectly every time. Advanced smart ovens, for example, can use sensors (and even internal cameras with image recognition) to identify what you’re cooking – be it a pizza, a chicken, or cookies – and then automatically set the appropriate temperature and cooking time. Throughout the cooking process, AI algorithms adjust the settings on the fly: they might lower the heat if a roast is cooking faster than expected or switch to a warming mode once a dish is done to prevent overcooking. AI-enabled cookers and multicookers (like smart pressure cookers or rice cookers) similarly modulate their settings based on the type and quantity of food, taking into account factors that a user might not even think of, such as altitude or humidity. This level of smart automation means even novice cooks can achieve consistent, professional-quality results because the appliance essentially “knows” how to cook the dish correctly. The technology also improves safety – an AI oven can shut itself off once food is done, and some can send alerts if they detect something abnormal (like smoke or an empty pot left on the burner). By simplifying the cooking process and reducing human error, AI-powered kitchen appliances allow for convenient meal preparation and can reduce food waste from failed cooking attempts.
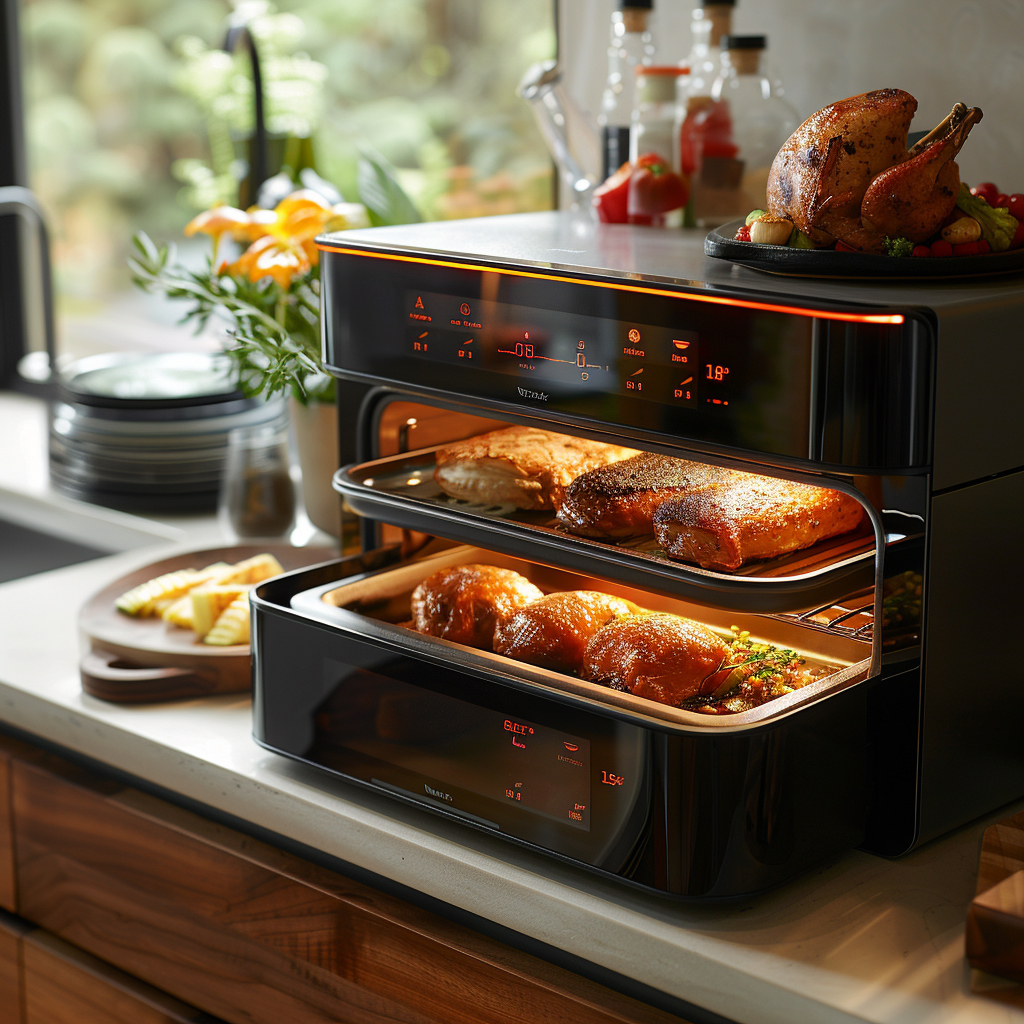

The market for smart kitchen appliances has been growing rapidly. In 2023, global sales of smart appliances (which include cooking devices like AI-assisted ovens and smart refrigerators) reached roughly $21.5 billion, up from about $17.8 billion in the previous year. Industry forecasts expect this trend to continue, with the smart kitchen sector projected to roughly double to around $43 billion by 2027, reflecting how quickly consumers are embracing AI in their kitchen gadgets.
9. Robotic Cleaners
Robotic cleaners like smart vacuums and mops have seen major improvements thanks to AI, which allows them to navigate homes efficiently and adapt to different cleaning needs. Early robot vacuums mostly bumped around randomly, but modern models use AI-driven mapping technology (often aided by lidar sensors or cameras) to create a floor plan of your home. They intelligently plan cleaning routes to ensure every area is covered in the least amount of time, avoiding redundancy. As they clean, AI helps them identify obstacles and furniture so they can go around them smoothly without getting stuck; many can now recognize specific objects on the floor (like cables or pet accidents) and steer clear. These robots also adjust their cleaning settings on the fly using AI: for instance, they can detect when they move from hardwood to carpet and automatically increase suction power, or do extra passes in high-traffic dirty areas. Over time, a robotic cleaner “learns” the layout and the typical dirt spots in a home, and it can optimize its patterns or suggest optimal cleaning schedules. Some even empty their dustbins autonomously and return to recharge when needed, then resume cleaning where they left off. The integration of AI has turned robotic cleaners into truly independent housekeepers that deliver consistently clean floors with minimal human intervention.

The demand for AI-assisted cleaning devices is surging. The global market for robotic vacuum cleaners reached about $9.1 billion in annual revenue in 2024, and it’s forecast to grow explosively – expected to cross approximately $31.7 billion by 2033 – as more households worldwide embrace autonomous cleaning robots in place of traditional vacuums.
10. Entertainment Recommendations
AI has become the cornerstone of entertainment recommendation systems in smart homes, fundamentally changing how people discover new movies, shows, and music. Streaming services on smart TVs (like Netflix, Disney+, etc.) and music platforms on smart speakers (like Spotify or Pandora) use collaborative filtering and other machine learning techniques to analyze what you’ve watched or listened to before. Based on patterns in your behavior and comparisons to millions of other users, the AI curates personalized suggestions for what you might enjoy next. These recommendations continuously update – for example, after you finish a TV series, the service might immediately suggest a similar genre or something starring the same lead actor. AI algorithms factor in subtle aspects of your taste, such as genres you gravitate towards at different times of day or week, and can even take into account contextual signals (like using a device’s time or location to infer if you might prefer upbeat music in the morning versus relaxing music at night). The more you use these services, the more the AI learns about your preferences, resulting in eerily accurate suggestions that often introduce you to content you end up loving. This personalized recommendation experience keeps users engaged and simplifies content discovery – instead of searching through hundreds of titles, great options are presented to you on your TV or smart display, curated by an AI that knows your entertainment profile.

AI-driven recommendation engines now guide the majority of viewing choices on streaming platforms. For example, about 75% of what people watch on Netflix is a result of the platform’s personalized recommendations (rather than direct searches or manual browsing), demonstrating how heavily users rely on AI suggestions to decide their entertainment in smart home environments.