1. Enhanced Facial Recognition Accuracy
AI algorithms have dramatically improved facial recognition accuracy by learning from vast and diverse datasets. Modern deep learning models can recognize faces under challenging conditions – varying lighting, angles, even partial obstructions – far better than earlier techniques. They continuously self-optimize by adjusting to new data, which means the system gets more accurate as it encounters more faces. This adaptability reduces false matches and missed identifications, making facial recognition a reliable authentication method. In practice, AI-enhanced facial recognition systems provide quick, touch-free verification with a high degree of confidence, even in busy real-world environments like airports and public venues.

AI-driven facial recognition now routinely achieves extremely high accuracy. According to the Security Industry Association, many leading facial recognition technologies used today are “well over 99%” accurate overall, and maintain over 97.5% accuracy across more than 70 diverse demographic variables. This marks a massive improvement over past generations – for instance, deep-learning face algorithms have improved so much that error rates dropped from about 4% in 2014 to effectively 0.1% or lower in recent evaluations. In U.S. government tests, dozens of current AI face recognition algorithms were able to correctly identify individuals more than 99% of the time when matching high-quality photos. These advances illustrate how AI has boosted facial recognition performance to a level on par with, or even exceeding, traditional biometric modalities in accuracy.
2. Adaptive Voice Recognition
AI makes voice recognition systems more adaptive and robust to changes in a user’s voice over time. Using machine learning, these systems “learn” a person’s vocal patterns and can account for variations due to aging, illness (like a cold), or fatigue. Background noise and different accents become less of a barrier as AI models are trained on diverse audio samples and can filter out irrelevant sounds. This means the voice biometric authentication remains accurate even if your voice sounds a bit different than usual. Overall, AI’s adaptive learning ensures voice recognition is both highly accurate and able to continuously fine-tune itself to the user, providing reliable hands-free security.

Advances in AI have greatly improved voice biometrics accuracy and speed. In fact, modern AI-powered speaker recognition systems can verify a person’s identity with about 99% accuracy from as little as half a second of speech. This level of performance is a direct result of deep learning models that extract unique vocal features and adapt to slight voice changes. Industry reports note that today’s voice authentication engines are so refined that they can distinguish a genuine user from an imposter even with very short voice snippets. For example, banks using AI voice ID in call centers have seen consistent authentication success rates in the high 90-percent range, enabling secure customer logins despite background noise or transient voice changes. These AI enhancements illustrate how voice recognition has become both highly accurate and resilient to everyday voice variability.
3. Fingerprint Analysis Improvement
AI has elevated fingerprint recognition by using advanced pattern-matching and image enhancement techniques. Traditional fingerprint systems could be thrown off by slight differences in finger placement, pressure, or skin conditions (like dryness or cuts). Now, AI algorithms analyze the minutiae – those tiny fingerprint ridge details – with much greater sophistication, filtering out noise and highlighting the true pattern. They can even reconstruct or clarify partial or low-quality prints. The result is that fingerprint scanners reject fewer legitimate users due to minor variances and are more consistent in identifying the correct fingerprint on the first try. This improvement makes fingerprint authentication faster and more reliable for everyday use.
Fingerprint biometrics were already a mature technology, but AI has pushed their accuracy to new heights. U.S. government evaluations report that today’s state-of-the-art fingerprint matching systems achieve between 98.1% and 99.9% accuracy in identifying individuals from prints. In other words, modern algorithms correctly match fingerprints almost every time, with vanishingly few errors. The FBI’s Next Generation Identification (NGI) system, for example, upgraded its algorithms and saw fingerprint match rates climb to over 99% accuracy – a notable jump from prior systems. These AI-enhanced fingerprint systems are also better at handling poor impressions or partial prints, significantly reducing false rejections due to issues like dry skin or uneven finger pressure. The near-perfect accuracy and robustness of AI-driven fingerprint analysis underscore how much more dependable this biometric modality has become in recent years.
4. Iris Recognition Enhancement
AI is greatly improving iris scan authentication, which uses the unique patterns in the colored part of the eye. New AI-based iris recognition systems can handle real-world issues like glare on glasses, contact lenses, or slight movements. They use neural networks to enhance iris images by adjusting for reflections or blur, ensuring the iris pattern is captured clearly. AI also allows the system to adapt if a person’s iris texture changes slightly with age or health. These enhancements mean iris scanners are faster and more accurate, working reliably even if you’re wearing eyewear or if the scan is taken in less-than-ideal lighting. Ultimately, AI makes iris recognition an extremely secure yet practical biometric method, known for both its precision and improved user experience.
Iris recognition, already one of the most accurate biometrics, has been further boosted by AI-driven advancements. In late 2023, an American-developed AI iris system set a new benchmark by achieving 99.3% matching accuracy when searching both eyes simultaneously, at a false positive identification rate of just 1%. This result comes from the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s (NIST) IREX evaluations, where the AI-powered iris algorithm not only was highly accurate but also dramatically faster than previous versions. Such precision means that out of hundreds of iris comparisons, the system virtually never misidentifies someone. Similarly, other top iris recognition engines in 2023 have reported single-eye accuracy rates around 99–99.5% in lab testing, underscoring the consistency of this modality. Thanks to these AI enhancements, iris scanners can maintain extremely high accuracy in real-world deployments – even when users wear glasses or the images are captured in challenging conditions.
5. Behavioral Biometrics
AI has opened up new frontiers with behavioral biometrics – identifying people by how they behave rather than physical traits. These systems monitor patterns like how someone types on a keyboard, moves a mouse, or even how they walk (gait). AI algorithms establish a profile of normal behavior for each user by learning from continuous data. If an anomaly is detected (for example, someone else is typing in a distinctly different rhythm), the system flags a potential security issue. All of this happens in the background without active input from the user. The advantage is an extra layer of security that is passive and user-friendly: the legitimate user likely never notices it, but an impostor who doesn’t behave like that user can be caught in the act. AI’s ability to learn and update these behavioral profiles continually makes this approach very effective at catching fraud or unauthorized access.
AI-powered behavioral biometrics can recognize users with impressive accuracy by analyzing their unique interaction patterns. For example, studies have shown that keystroke dynamics – the way a person types – can be used to authenticate individuals with roughly 97% accuracy, with false acceptance and rejection rates under 3%. In one 2024 experiment, researchers trained machine learning models on users’ typing rhythms and mouse movements; the system was able to correctly distinguish legitimate users from impostors nearly all the time, only erring on rare occasions. Another study achieved over 98% accuracy on a dataset by using an AI model to learn a combination of typing speed, key press durations, and finger pressure patterns unique to each person. These results demonstrate that AI can capture subtle behavioral signatures – essentially a “digital fingerprint” of how we interact with devices – and use them to continuously verify identity. Major banks and financial platforms have reported significant fraud reductions by deploying such behavioral biometric systems, as they can silently detect when an account isn’t being operated by the true owner.
6. Anti-spoofing Measures
AI has become a critical tool in defending biometric systems against “spoofing” – attempts to fool sensors using fake fingerprints, photos, or masks. Traditional detection methods looked for static cues, but AI can analyze subtle signals of liveness or authenticity. For instance, AI-driven face recognition now checks for tiny facial movements (like eye blinks or skin texture changes) to ensure the subject is a live person and not a photograph or deepfake video. With fingerprints, AI can examine pores, sweat distribution, or temperature to tell a real finger from a silicone replica. These anti-spoofing algorithms continuously learn from new attack techniques, meaning they improve as hackers try new tricks. The outcome is a biometric system that’s much harder to fool – a would-be intruder can’t just hold up a photo or use a dummy fingerprint, because the AI will detect telltale signs of a spoof and reject the attempt, thereby greatly enhancing security.
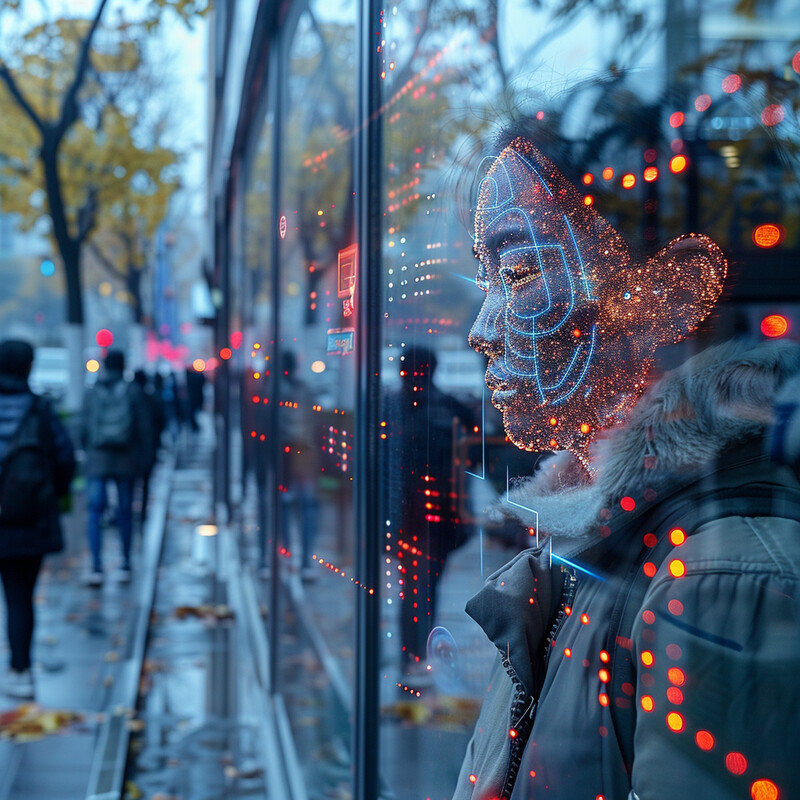

AI-enhanced anti-spoofing systems have greatly improved the ability to detect fraudulent biometric attempts. In a 2023 international challenge on face recognition security, the top AI models achieved an average classification error rate (ACER) as low as around 4–5% in distinguishing real faces from spoofing attacks. This corresponds to roughly 95% accuracy in catching fake attempts (such as photos, videos, or masks presented to the camera). For context, lesser algorithms in the past often had error rates well above 10% under similar “in the wild” conditions, indicating far more misses. Similarly, AI-based fingerprint liveness detection now correctly identifies over 90–99% of fake fingerprint attempts, according to industry evaluations, by analyzing features like blood flow and 3D tissue characteristics. These improvements are evident in real-world deployments: for example, many modern smartphones use AI-driven face unlock that will not be fooled by a mere photograph – a testament to the sophisticated liveness checks in place. Overall, the integration of AI in anti-spoofing has drastically reduced the success rate of biometric forgeries, closing loopholes that fraudsters previously exploited.
7. Real-Time Decision Making
AI enables biometric authentication to happen in real-time, even in high-traffic settings. In practice, this means systems can capture a biometric sample (like a face image or fingerprint), compare it against the database, and confirm identity almost instantaneously. The speed comes from AI algorithms optimized for fast pattern matching and running on specialized hardware. For users, it feels seamless – a door unlocks the moment you appear in front of the camera, or you pass through a checkpoint without pausing. Real-time processing is crucial in places like airports or offices, where any delay could cause bottlenecks. AI’s ability to quickly yet accurately make these authentication decisions ensures security checks don’t slow people down. This blending of speed and accuracy is something older biometric systems struggled with, but modern AI-powered ones excel at, to the point that identity verification is virtually frictionless.
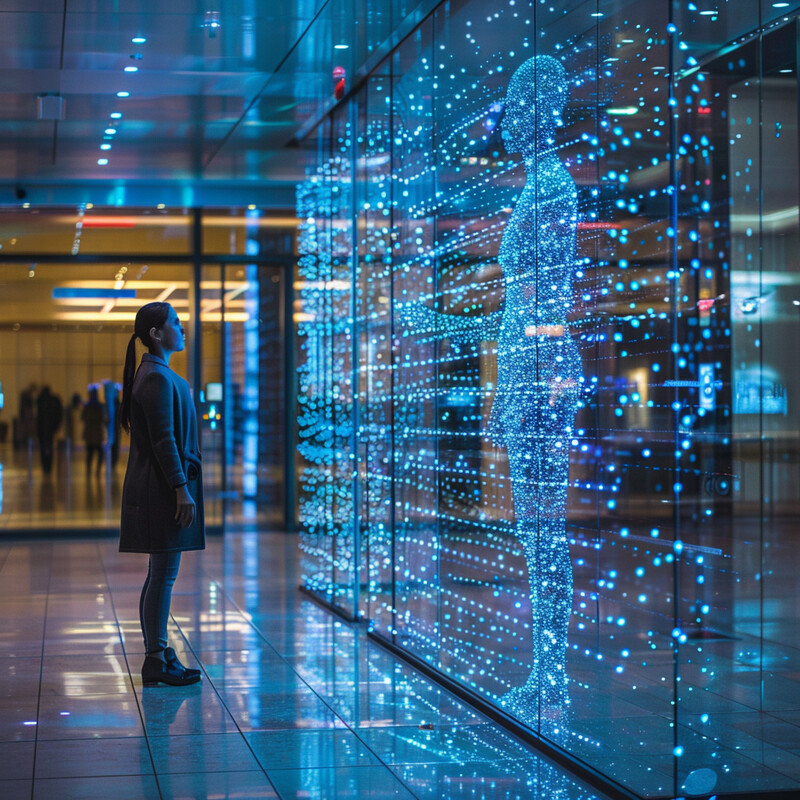

Biometric systems powered by AI can now process and respond with lightning speed, even at national scales. A striking example is the use of facial recognition at U.S. border checkpoints: as of 2023, U.S. Customs and Border Protection has used AI-based facial comparison to process over 300 million travelers in real time, and in doing so has intercepted more than 1,800 impostors attempting to enter with false identities. This real-world deployment highlights how AI enables immediate decision-making – each traveler’s face is scanned and matched against official photo records within a second or two. The system’s speed and accuracy were such that dozens of identity fraudsters were caught that a slower, manual process might have missed. Likewise, airports implementing AI biometric boarding have reported boarding process times cut by 30% or more, since verification happens almost instantaneously when a passenger steps in front of the camera. These statistics demonstrate that AI-driven biometrics can handle enormous volumes of people with virtually instant decisions, drastically improving operational efficiency while maintaining high security standards.
8. Integration with Other Security Measures
AI helps weave biometrics into multi-factor authentication frameworks, strengthening overall security. Instead of relying on just one method (like a fingerprint or a password), AI can coordinate several methods at once. For example, a system might use your fingerprint plus a one-time PIN, deciding with AI logic if both factors check out or if additional verification is needed based on risk. AI can also analyze context – such as the user’s location or device – to adjust security requirements on the fly. By integrating biometrics (what you are) with traditional factors (what you have or know), AI builds a layered defense that is much harder for attackers to breach. Even if one factor is compromised, the AI will catch abnormal patterns or require the other factors, thwarting unauthorized access. This intelligent fusion of biometric data with other security measures results in a more resilient authentication process without piling on too much inconvenience for legitimate users.
Combining AI with biometric and traditional security measures has been shown to greatly reduce security breaches. A recent industry report by Deloitte found that banks implementing AI-enhanced biometric security systems experienced 37% fewer successful cyber-attacks compared to similar institutions using only conventional (non-biometric) authentication. In practical terms, these banks saw significantly lower instances of account takeovers and fraud once AI started cross-verifying logins with biometrics alongside passwords or tokens. The AI analyzes multiple inputs – for instance, confirming the user’s fingerprint or facial data in addition to their PIN – and only grants access if the combination fits the expected pattern. This multi-layered approach, guided by AI risk analysis, has led to concrete improvements: financial organizations report major drops in fraud losses and unauthorized account access when biometrics are integrated as a second factor. The 37% figure highlights how effective this synergy is, as nearly half of would-be breaches were prevented by the added biometric checks. It underscores that AI not only boosts biometric accuracy, but when used to integrate different security methods, it measurably strengthens protection against attacks.
9. Continuous Authentication
AI enables continuous authentication, meaning the system doesn’t just verify you once at login and then stop – it keeps checking in the background that the user is the same throughout the session. This is done by constantly monitoring biometric signals like typing behavior, mouse movements, or even periodic face snapshots, all without disrupting the user. AI models compare these ongoing inputs to the profile of the legitimate user. If a mismatch is detected – say someone else takes over the computer – the system can automatically lock out or request re-authentication. Continuous authentication is especially valuable for sensitive systems, as it can catch scenarios like an intruder taking over a logged-in session. AI’s role is crucial here because it can handle the stream of data and make real-time judgments about whether the current user’s behavior deviates from the norm. This approach greatly enhances security during long or unattended sessions while remaining unobtrusive to the genuine user.

Continuous authentication systems powered by AI have demonstrated robust performance in verifying user identity throughout a session. In one 2024 experiment, a reinforcement learning-based continuous authentication model was able to maintain up to 93.5% accuracy on test data while monitoring users’ behaviors in real time. The system tracked factors like keystroke timing and pointer movements continuously; its false accept rate was low (on the order of a few percent) and it quickly detected when an imposter attempted to assume control, even after the initial login. Other academic studies similarly report that AI-driven continuous verification can detect unauthorized users within seconds with over 90% accuracy, by comparing ongoing behavioral biometrics against the legitimate user’s pattern. For example, if an intruder starts using a workstation, their different typing speed and mouse usage can trigger an alert or lockout almost immediately once the AI model recognizes the deviation. Organizations implementing these continuous AI authentication measures (often alongside traditional login steps) have noted improved security – one case study showed that adding continuous behavioral monitoring reduced insider misuse incidents and session hijacking events, providing an extra safety net after the initial login. These outcomes highlight that AI can effectively keep watch and confirm user identity non-stop, not just one-and-done at login time.
10. Personalization of User Experience
Beyond security, AI uses biometric recognition to personalize services for individuals. Once you’re identified by your biometric (say, face or fingerprint), the system can tailor the interface or settings to you. For example, a smart home might recognize who just walked in and automatically adjust lighting, temperature, or play that person’s favorite music. In banking apps, after a biometric login, the AI might present a customized dashboard based on the user’s habits. This fusion of identification and personalization creates a smoother, more user-friendly experience because the service “knows” who you are instantly and can anticipate your needs or preferences. Importantly, AI handles this personalization in a secure way, ensuring that only the right person gets their specific profile or settings. The result is that authentication doubles as a personalization trigger – logging in isn’t just about gaining access, it also seamlessly transitions into an individualized session, enhancing convenience and satisfaction.
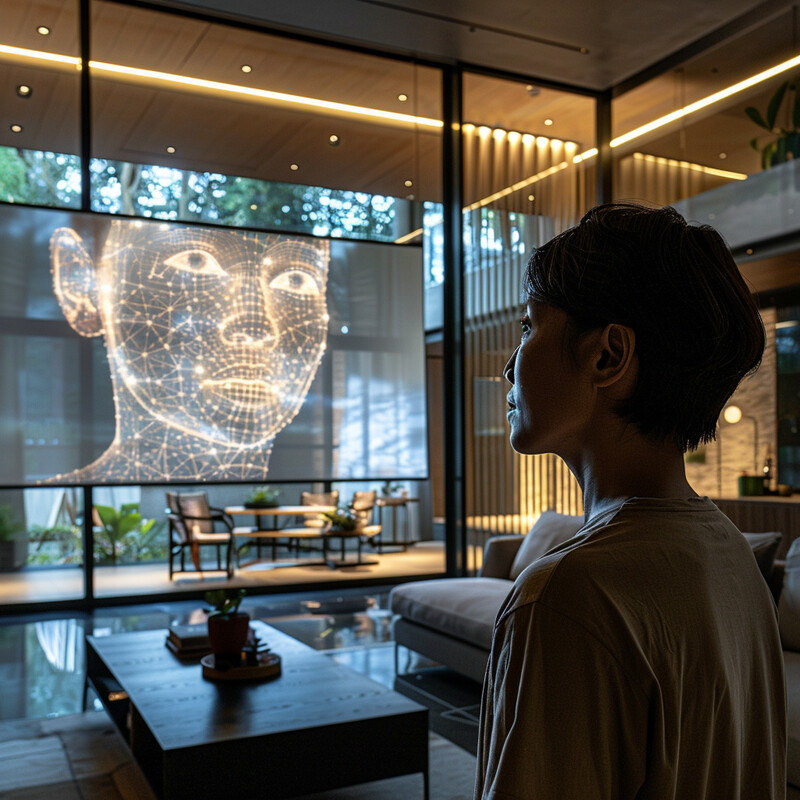

Biometric authentication through AI is not only making systems secure but also improving user satisfaction by enabling personalized, frictionless experiences. A clear indicator comes from the banking sector: a 2023 J.D. Power study found that financial institutions which implemented biometric logins saw a 23% increase in customer satisfaction with their digital banking services compared to those using traditional login methods. Customers appreciated the ease of logging in with a fingerprint or face scan and, once recognized, being greeted with their personalized account overview immediately. In practice, removing password hassles and instantly loading user-specific preferences (made possible by AI recognizing the individual) translates into a better user experience. This trend isn’t limited to banking; similar surveys have shown that users of smartphones and laptops prefer biometric unlock because it’s fast and brings them straight to their personal home screen or workspace. Companies report higher engagement and retention when they personalize content after a biometric sign-in – for instance, streaming services that log in via face recognition can automatically switch to the correct viewer’s profile, presenting their watchlist without extra steps. The significant jump in satisfaction scores underscores that people value the convenience and personal touch that AI-driven biometrics provide, making security feel seamless rather than burdensome.