1. Automated Cataloging and Classification
AI algorithms can analyze and categorize library materials based on their content, metadata, and user interactions, streamlining the cataloging process and ensuring materials are easily accessible.

By utilizing AI for automated cataloging and classification, librarians can significantly enhance the efficiency of organizing library materials. This technology allows for rapid processing of new and existing collections, ensuring that books, journals, and digital resources are accurately categorized and easily discoverable. Librarians can devote more time to user engagement and personalized services, rather than manual cataloging tasks, improving overall library operations and user satisfaction.
2. Semantic Search and Discovery
AI enhances search capabilities by understanding the context and semantics behind user queries, improving the accuracy of search results and helping users discover relevant materials more efficiently.

Implementing AI-driven semantic search tools enables librarians to offer a more intuitive and effective discovery experience for library users. By understanding the context and nuances of search queries, AI enhances the relevance of search results, helping users find the information they need more quickly. This capability allows librarians to assist researchers and patrons in navigating vast collections more efficiently, promoting a deeper exploration of available resources.
3. Recommendation Systems
By analyzing user behavior and preferences, AI can recommend books, articles, and other resources tailored to individual interests, facilitating discovery and exploration within the library's collection.

Librarians can leverage AI-powered recommendation systems to guide patrons toward materials that match their interests and research needs. These systems analyze user behavior and preferences to suggest books, articles, and other resources, creating a personalized library experience. This not only enhances user engagement but also encourages the discovery of new topics and authors, enriching the educational and recreational value of the library.
4. Natural Language Processing for Query Assistance
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can interpret natural language queries from users, providing accurate answers and guidance on utilizing library resources and services.

By adopting AI chatbots and virtual assistants that understand natural language, librarians can provide round-the-clock support to answer queries, guide research, and navigate library services. This technology ensures that help is always available, even outside of traditional library hours, improving access to information and making library resources more user-friendly for a diverse patron base.
5. Predictive Analytics for Collection Development
AI analyzes borrowing patterns, research trends, and external data sources to predict future resource needs, aiding libraries in making informed decisions about collection development and resource allocation.
Utilizing predictive analytics, librarians can make data-driven decisions about collection development and resource allocation. AI analyzes trends in borrowing patterns, research interests, and external data to forecast future resource demands. This insight allows librarians to strategically expand their collections to meet the evolving needs of their communities, ensuring that valuable resources are available and accessible.
6. Digitization and Preservation
AI tools can automate the digitization of physical materials, including text recognition and correction, making rare and fragile resources available digitally while preserving the original items.
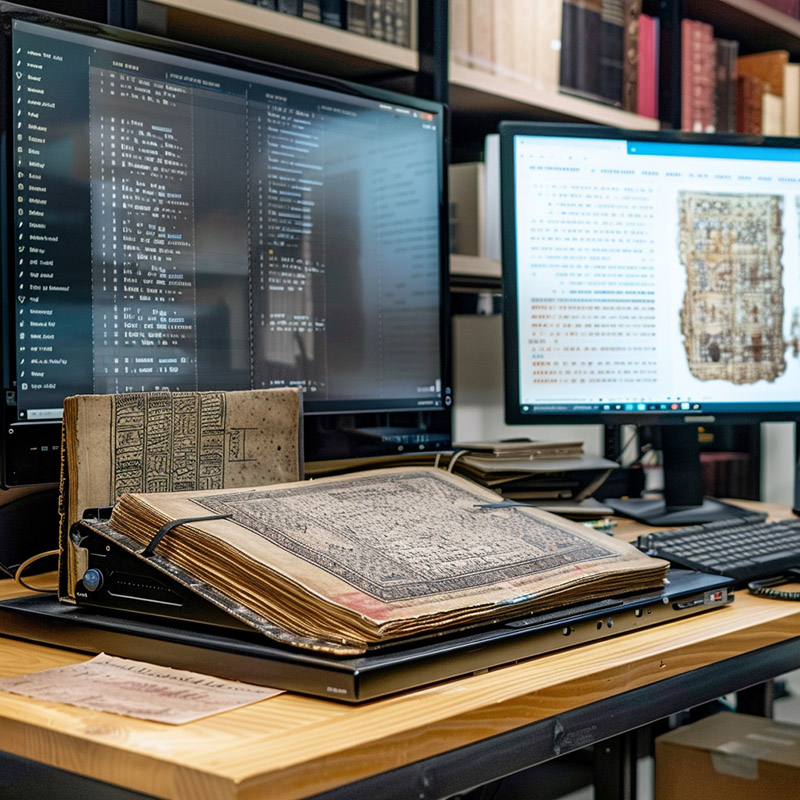

AI tools that automate the digitization of library materials not only expedite the preservation of rare and fragile items but also enhance the accessibility of these resources. Librarians can oversee the digitization process, ensuring that historical documents, books, and artifacts are available to a global audience without risking damage to the original items, thereby extending the library's reach and impact.
7. User Behavior Analysis
AI systems analyze user engagement and interaction within the library, providing insights into how resources are used and identifying opportunities to enhance services and user experience.
By analyzing user behavior with AI, librarians can gain insights into how patrons interact with library resources and services. This information helps in tailoring library offerings to better match user preferences and identifying areas for improvement. Enhanced understanding of user behavior supports the development of more responsive and user-centric library services, fostering a more engaging library environment.
8. Accessibility Enhancements
AI-driven tools, such as voice-to-text and text-to-speech conversion, improve accessibility for users with disabilities, ensuring equitable access to library materials and information.
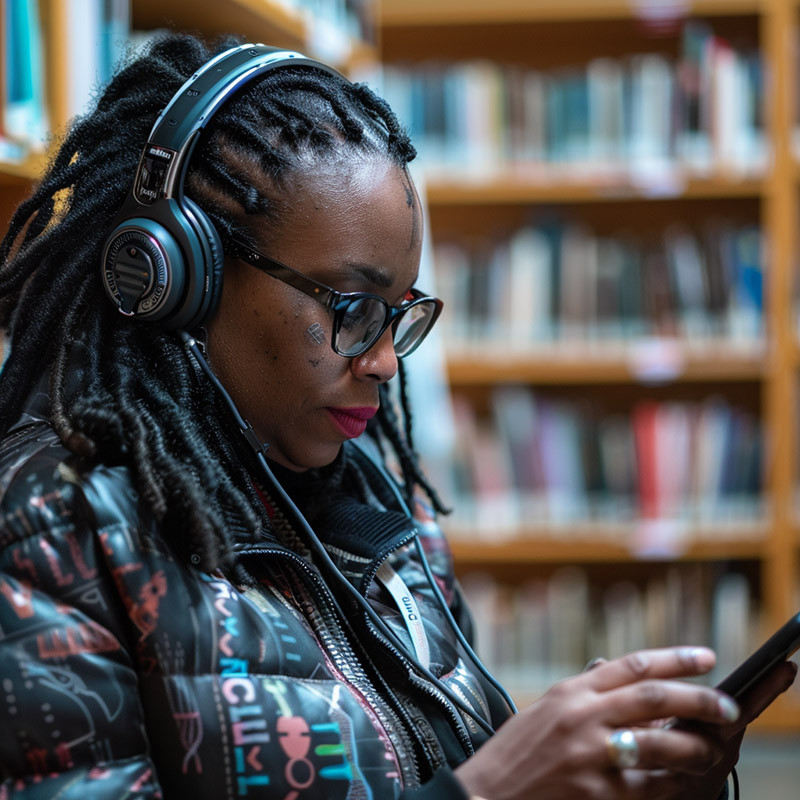

AI-driven accessibility tools, such as voice-to-text and text-to-speech conversion, enable librarians to make library collections more accessible to individuals with disabilities. By implementing these technologies, libraries can ensure equitable access to information for all users, promoting inclusivity and removing barriers to knowledge.
9. Content Analysis for Research Support:
AI can assist researchers by analyzing large volumes of text or data, identifying patterns, trends, and relationships that might not be immediately apparent, supporting academic research and analysis.

Librarians can assist researchers more effectively by employing AI for content analysis. This technology can sift through large volumes of text to identify trends, patterns, and connections, providing valuable insights for academic research. By offering AI-assisted research support, librarians facilitate deeper scholarly exploration and contribute to the advancement of knowledge across disciplines.
10. Fraud Detection and Intellectual Property Protection
AI algorithms monitor and analyze usage data to detect unusual patterns that may indicate copyright infringement or misuse of digital materials, helping libraries protect intellectual property rights.

Leveraging AI for fraud detection and intellectual property protection, librarians can safeguard digital collections and ensure compliance with copyright laws. This proactive approach to monitoring usage and detecting unauthorized access helps maintain the integrity of library resources. By protecting intellectual property, librarians uphold the ethical standards of information sharing and preserve the trust of content creators and users alike.